Body Language of Full Body Hug or Embrace
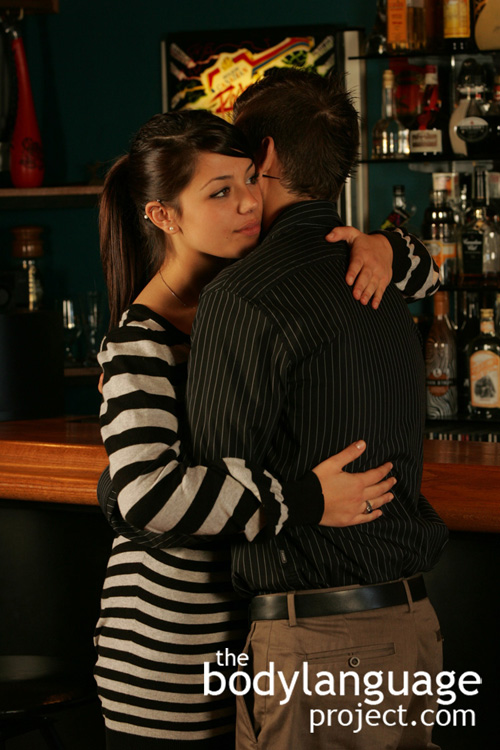 Cue: Full Body Hug
Cue: Full Body Hug
Synonym(s): Embrace, Hip-To-Hip Hug, Sexual Hug, Hugging Sexually.
Description: This is one of two types of hugs. In this hug, the chests of each person makes contact, but more telling is the pressing together of the hips.
In One Sentence: The full body hug signifies sexual interest and high intimacy.
How To Use it: Testing the willingness to take part in a full hug can indicate the level of attraction between two people. For example, at the end of a date, a man may offer a kiss on the cheek and come in for a hug. If she permits their hips to connect, it’s a strong indication that she truly finds him attractive. On the other hand, should she maintain separation between her hips and his, he should assume that things are progressing more slowly. A large distance, on the other hand, indicates platonic feelings or even dislike. Therefore, the degree of separation between the hips is a good indication of the level of romance.
Context: Dating.
Verbal Translation: “I like you enough to press my entire body against yours, including our hips and genitals.”
Variant: See Hug.
Cue In Action: Dave and Scarlet had been dating for a while. When they hugged their torsos engulfed each others and their hip were tightly pressed together. On their first date, they only leaned in and touched each others shoulders together. Their feelings for each other had changed.
Meaning and/or Motivation: The full body hug is reserved for sexual partners and occurs with full chest-to-chest and hip-to-hip contact. The meaning is sexual in nature. Those who hug by pressing their hips together are telling each other that they are comfortable touching genital-to-genital.
The full hug is a reliable indicator of sexual interest and is never seen with family or friends. Simply by examining how a pair hugs, can tell others what sort of feelings are present. When family members and friends hug they will press their shoulders together and force their hips back and away to protect them from contact. A hug test at the end of the date will tell prospective mates what level of attraction is present.
Cue Cluster: This is a powerful and reliable stand-alone cue of intimacy and requires no additional cues.
Body Language Category: Courtship displays, Comfort body language, Indicators of sexual interest (IOsI), Intimate touching, Intention movements, Liking.
Resources:
Bowlby, J. (1979). The making and breaking of affectional bonds. British Journal of Psychiatry, 130, 201 -210, 42 1-43 1 .
Broome, Marion E.. Helping Parents Support Their Child In Pain. Pediatric Nursing. 2000. 26(3): 315.
Bernal, Gilda Rios ; Wortham, Suec. How to Calm Children through Massage. Childhood Education. 1997. 74(1): 9-14.
Bohm. 1997. Effects of interpersonal touch, degree of justification, and sex of participant on compliance with a request. The Journal of social psychology. 137: 460-469.
Derlega, Valerian ; Lewis, Robin ; Harrison, Scott ; Winstead, Barbara ; Costanza, Robert. Gender differences in the initiation and attribution of tactile intimacy. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior. 1989. 13(2): 83-96.
Derlega, Valerian J. ; Catanzaro, Diane ; Lewis, Robin J. Lisak, David (editor). Perceptions About Tactile Intimacy in Same-Sex and Opposite-Sex Pairs Based on Research Participants’ Sexual Orientation. Psychology of Men & Masculinity, 2001, Vol.2(2), pp.124-132
Debrot, Anik ; Schoebi, Dominik ; Perrez, Meinrad ; Horn, Andrea B. Touch as an interpersonal emotion regulation process in couples’ daily lives: the mediating role of psychological intimacy. Personality & social psychology bulletin. 2013. 9(10): 1373-85.
Dickinson, Amy. Block That Hug: The rules on touching children have changed for parents who volunteer as coaches or tutors.(Personal Time/Your Family)(Brief Article). Time. 2000. 155(14): 142.
Fisher, J; Rytting, M and Heslin, R. 1976. Hands touching hands: affective and evaluative effects on interpersonal touch, Sociometry 39: 416–421.
Feldman, R., Singer, M.,& Zagoory, O. (2010). Touch attenuates infants’ physiological reactivity to stress. Developmental Science, 13(2), 271–278.
Fromme, Donald ; Jaynes, William ; Taylor, Deborah ; Hanold, Elaine ; Daniell, Jennifer ; Rountree, J. ; Fromme, Marie. Nonverbal behavior and attitudes toward touch. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior. 1989. 13(1): 3-14.
Flores, Luis E. ; Berenbaum, Howard. Desire for emotional closeness moderates the effectiveness of the social regulation of emotion. Personality and Individual Differences
Floyd, Kory. All Touches are not Created Equal: Effects of Form and Duration on Observers’ Interpretations of an Embrace. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior. 1999. 23(4): 283-299.
Guéguen, N. (2007). Courtship compliance: The effect of touch on women’s behavior. Social Influence, 2, 81-97.
Gueguen, Nicolas. The effect of a woman’s incidental tactile contact on men’s later behavior.(Report). Social Behavior and Personality: an international journal. 2010. 38(2): 257(10).
Guéguen, Nicolas. Nonverbal encouragement of participation in a course: the effect of touching Social Psychology of Education. 2004. 7: 89–98.
http://bodylanguageproject.com/articles/a-touching-way-to-encourage/
Gurevitch, Z. D. The Embrace: On the Element of Non-Distance in Human Relations. The Sociological Quarterly. 1990. 31(2): 187-201.
Golden, Deborah. Hugging the Teacher: Reading Bodily Practice in an Israeli Kindergarten. Teachers and Teaching: Theory and Practice. 2004. 10(4): 395-407.
Gulledge, Andrew K ; Stahmann, Robert F ; Wilson, Colwick M. Seven types of nonsexual romantic physical affection among Brigham young university students
Psychological reports 2004, Vol.95(2), pp.609-14
Gulledge, Andrewk. ; Gulledge, Michelleh. ; Stahmannn, Robertf. Romantic Physical Affection Types and Relationship Satisfaction. The American Journal of Family Therapy, 2003, Vol.31(4), p.233-242
Greenbaum, Paul ; Rosenfeld, Howard. Varieties of touching in greetings: Sequential structure and sex-related differences. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior. 1980. 5(1): 13-25.
Gulledge, Andrewk. ; Gulledge, Michelleh. ; Stahmannn, Robertf.. Romantic Physical Affection Types and Relationship Satisfaction. The American Journal of Family Therapy. 2003. 31(4): 233-242.
Gulledge, Andrew K ; Stahmann, Robert F ; Wilson, Colwick M. Seven types of nonsexual romantic physical affection among Brigham young university students. Psychological reports. 2004. 95(2): 609-14.
Hansen, Jacqueline. Teaching without talking: teachers need to be aware of more than just the words they speak to children. They also need to monitor the nonverbal messages that they’re sending to students through proximity, eye contact, gestures, and touching. Phi Delta Kappan. 2010. 92(1): 35(6).
Hosey, Geoffrey ; Thompson, Robin. Grooming and touching behaviour in captive ring-tailed lemurs ( Lemur catta L.). Primates. 1985. 26(1): 95-98.
Hazan, C., & Shaver, P. (1987). Romantic love conceptualized as an attachment process. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 52, 511–524.
Hansen, Jacqueline. The Truth about Teaching and Touching. Childhood Education. 2007. 83(3): 158-162.
Hadi, Rhonda ; Valenzuela, Ana. A meaningful embrace: Contingent effects of embodied cues of affection. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 2014, Vol.24(4), pp.520-532
Heino, William J. Perfect Timing for Parental Hugs.(to comfort children following medical treatment)(Brief Article). Consultant. 2000. 40(13): 2173.
Hugs help protect against stress and infection, say Carnegie Mellon researchers.(Report)
Health & Medicine Week, Jan 2, p.1341
Hernandez-Reif, Maria ; Diego, Miguel ; Field, Tiffany. Preterm infants show reduced stress behaviors and activity after 5 days of massage therapy. Infant Behavior and Development. 2007. 30(4): 557-561.
Harrison, Lynda Law. The use of comforting touch and massage to reduce stress for preterm infants in the neonatal intensive care unit. Newborn and Infant Nursing Reviews. 2001. 1(4): 235-241.
Hennessy, Michael B ; T. Williams, Michael ; Miller, Deborah D ; Douglas, Chet W ; Voith, Victoria L. Influence of male and female petters on plasma cortisol and behaviour: can human interaction reduce the stress of dogs in a public animal shelter?
Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 1998. 61(1): 63-77.
Kammers, Marjolein P.M. ; de Vignemont, Frédérique ; Haggard, Patrick. Cooling the Thermal Grill Illusion through Self-Touch. Current Biology. 2010. 20(20): 1819-182.
Karagozoglu, Serife ; Kahve, Emine. Effects of back massage on chemotherapy-related fatigue and anxiety: Supportive care and therapeutic touch in cancer nursing. Applied Nursing Research. 2013. 26(4): 210-217.
Landau, Rivka. Affect and attachment: Kissing, hugging, and patting as attachment behaviors. Infant Mental Health Journal. 1989. 10(1): 59-69.
Larsen, Knuds. ; Leroux, Jeff. A study of same sex touching attitudes: Scale development and personality predictors. Journal of Sex Research. 1984. 20(3): 264-278.
Moszkowski, Robin J. ; Stack, Dale M. ; Girouard, Nadine ; Field, Tiffany M. ; Hernandez-Reif, Maria ; Diego, Miguel. Touching behaviors of infants of depressed mothers during normal and perturbed interactions. Infant Behavior and Development. 2009. 32(2): 183-194.
Maclaren, Kym. Touching matters: Embodiments of intimacy. Emotion, Space and Society. 2014. 13: 95-102.
Madden, Myron. Meaningful pastoral intimacy. Pastoral Psychology. 1976. 25(1): 34-38.
Maclaren, Kym. Touching matters: Embodiments of intimacy. Emotion, Space and Society. 2014. 13: 95-102.
Moore, Monica. Courtship Signaling and Adolescents: Girls Just Wanna Have Fun. Journal of Sex Research. 1995. 32(4): 319-328.
http://bodylanguageproject.com/articles/girls-just-want-to-have-fun-the-origins-of-courtship-cues-in-girls-and-women/
Moszkowski, Robin J. ; Stack, Dale M. ; Chiarella, Sabrina S. Infant touch with gaze and affective behaviors during mother–infant still-face interactions: Co-occurrence and functions of touch. Infant Behavior and Development. 2009. 32(4): 392-403.
Nelson, Holly ; Geher, Glenn. Mutual Grooming in Human Dyadic Relationships: An Ethological Perspective. Current Psychology. 2007. 26(2): 121-140.
O’sullivan, Lucia F. ; Cheng, Mariah Mantsun ; Harris, Kathleen Mullan ; Brooks-gunn, Jeanne. I Wanna Hold Your Hand: The Progression of Social, Romantic and Sexual Events in Adolescent Relationships. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health. 2007. 39(2): 100-107.
Paulsell, Shari ; Goldman, Morton. The Effect of Touching Different Body Areas on Prosocial Behavior. The Journal of Social Psychology. 1984. 122(2): 269-273.
Peck, J., & Shu, S. B. (2009). The effect of mere touch on perceived ownership. Journal of Consumer Research, 36(Oct), 434–447.
Rabinowitz, Fredric E. The male-to-male embrace: breaking the touch taboo in a men’s therapy group. Journal of Counseling and Development. 1991. 69(6): 574(3).
Remland, Martins. ; Jones, Tricias. ; Brinkman, Heidi. Interpersonal Distance, Body Orientation, and Touch: Effects of Culture, Gender, and Age. The Journal of Social Psychology. 1995 135(3): 281-297.
Rubin, Mark Morrison, Todd G. (editor). Social Affiliation Cues Prime Help-Seeking Intentions. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science/Revue canadienne des sciences du comportement. 2011. 43(2): 138-141.
Rempel, J., Holmes, J., & Zanna, M. (1985). Trust in close relationships. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 49, 95–112.
Shimooka, Yukiko ; Nakagawa, Naofumi. Functions of an unreported “rocking-embrace” gesture between female Japanese Macaques ( Macaca fuscata ) in Kinkazan Island, Japan. Primates. 2014. 55(2): 327-335.
Shelton, Kathryn ; Mckenzie, Richard B. Pedophiles and the regulation of hugging: concerns about protecting children may deprive them of important physical contact.(PUBLIC SAFETY). Regulation. 2012. 35(4): 14(5).
Shimooka, Yukiko ; Nakagawa, Naofumi. Functions of an unreported “rocking-embrace” gesture between female Japanese Macaques ( Macaca fuscata ) in Kinkazan Island, Japan. Primates. 2014. 55(2): 327-335.
Toronto, Ellen L.K. A clinician’s response to physical touch in the psychoanalytic setting. International Journal of Psychotherapy. 2002 7(1): 69-81.
Takeuchi, Mika ; Miyaoka, Hitoshi ; Tomoda, Atsuko ; Suzuki, Masao ; Liu, Qingbo ; Kitamura, Toshinori. The Effect of Interpersonal Touch During Childhood on Adult Attachment and Depression: A Neglected Area of Family and Developmental Psychology? Journal of Child and Family Studies. 2010. 19(1): 109-117.
Taavoni, S ; Shahali, S ; Haghani, H. Infant Vaccination Pain Management: Comparing the Effect of Mother’s Hug and Breast Feeding, Tehran, 2009-2010. Pediatric Research. 2011. 70: 738-738.
Tracy, R. L., & Ainsworth, M. D. S. (1981). Maternal affectionate behavior and infant-mother attachment patterns. Child Development, 52, 1341-1343.
Williams, Trish ; Connolly, Jennifer ; Cribbie, Robert. Light and Heavy Heterosexual Activities of Young Canadian Adolescents: Normative Patterns and Differential Predictors.(Author abstract)(Report). Journal of Research on Adolescence. 2008. 18(1): 145(28).
Willis, Frank N. , Jr. ; Dodds, Rebecca A. Age, relationship, and touch initiation. The Journal of Social Psychology. 1998. 138(1). 115(9).
 Cue: Intimate Gaze (The) or Triangular Gaze Pattern
Cue: Intimate Gaze (The) or Triangular Gaze Pattern