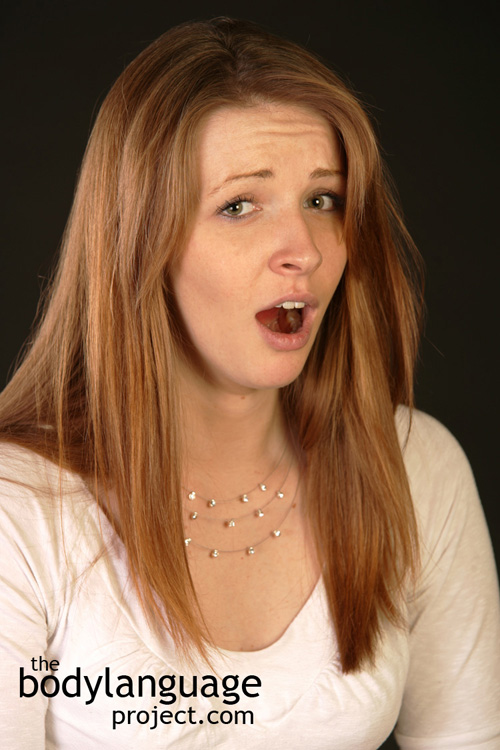
Body Language of Tongue Jutting or Pushing The Tongue Through Compressed Lips

 Cue: Tongue Jutting or Pushing The Tongue Through Compressed Lips.
Cue: Tongue Jutting or Pushing The Tongue Through Compressed Lips.
Synonym(s): Pushing The Tongue Through Compressed Lips.
Description: When the tongue is pushed through compressed lips.
In One Sentence: Sticking out the tongue through compressed lips signals that one has gotten away with something.
How To Use it: Sticking out the tongue can show that we’re joking a not to be taken seriously. This can produce a bonding effect by sharing in a joke.
However, if we’re not careful, we may stick our tongue out to admit our failure in being good spirited and have been caught in a misdeed.
Finally, the tongue jut is a way to show others that we disagree and are “rejecting” them or their ideas.
Context: a) General b) Dating.
Verbal Translation: “I’m sticking out my tongue through my lips because I’ve gotten away with this”, “I’m telling a cheeky joke or making a cheeky statement”, “I’ve made a mistake” or “I’ve been caught trying to pull a fast one.”
Variant: See Tongue Protrusion or Tongue Rejection.
Cue In Action: a) The friend spiked his buddy’s drink. As he grew more inebriated and began to stumble, his budding confronted him. He admitted to adding a bit extra to the drink. He followed his statement up by sticking his tongue out which he quickly clamped shut – he enjoyed watching his reaction. b) She wasn’t into him – her first reaction was to jut her tongue out showing her distaste.
Meaning and/or Motivation: Tongue jutting or tongue through compressed lips is used to signal a cheeky attitude when done amongst friends, but has a more sinister connotation in competitive situations since it indicates that a person has gotten away with something. “Tongue-jutting” is an indication that people figure they have gotten away with something, or have been caught doing something they shouldn’t have. However, in this case, the tongue is usually pushed through the teeth and doesn’t touch the lips.
The tongue jut gesture will be seen at the conclusion of an event such as signing a contract or winning a hand at poker by bluffing. Most of the time tongue protrusion happens when people feel they haven’t been caught, but sometimes it’s actually because they’ve been caught. Tongue through the lips or teeth can happen any place at anytime but signals the same thing almost every time, and that is that a person is doing something that is pushing the envelope of acceptability or has gotten caught doing something that is unacceptable.
If we notice this “tongue language” we should review what has been said. We may begin be assuming that we have been fooled, cheated or that we or someone around us has been made the butt of a joke. Lastly, we may surmise that tongue protruder, themselves, have made a mistake and it has come to their attention.
Cue Cluster: Watch for a goofy grin or smirk. When it spells rejection watch for head turned away, eyes averted or sneering nose.
Body Language Category: Automatic gesture, Dislike (nonverbal), Doubt or disbelief body language, Hostile body language, Inborn behaviours, Indicators of disinterest (IOD), Leaked or involuntary body language, Microgestures, Negative body language, Rejection body language.
Resources:
Andric, Michael ; Solodkin, Ana ; Buccino, Giovanni ; Goldin-Meadow, Susan ; Rizzolatti, Giacomo ; Small, Steven L. Brain function overlaps when people observe emblems, speech, and grasping. Neuropsychologia, 2013, Vol.51(8), pp.1619-1629
Alibali, M.W., Heath, D.C., and Myers,H.J. (2001). Effects of visibility between speaker and listener on gesture production: Some gestures are meant to be seen. Journal of Memory and Language, 44, 169–188.
Bernardis, P.,& Gentilucci,M.(2006).Speech hand gestures are the same communication system. Neuropsychologia, 44, 178–190.
Beattie, G., & Shovelton,H.(1999). Mapping the range of information contained in the iconich and gestures that accompany spontaneous speech. Journal of Language and social Psychology, 18, 438–462.
Cassell, J., & Thórisson, K. R. (1999). The power of a nod and a glance: Envelope vs. emotional feedback in animated conversational agents. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 13, 519–538.
Chandler, Jesse ; Schwarz, Norbert. How extending your middle finger affects your perception of others: Learned movements influence concept accessibility. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology. 2009. 45(1): 123-128.
http://bodylanguageproject.com/articles/how-extending-the-middle-finger-affects-perception/
Curtis V, Aunger R, Rabie T (2004) Evidence that disgust evolved to protect from risk of disease. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B 271: S131–S133. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2003.0144. PubMed: 15252963.
Curtis, V., & Biran, A. (2001). Dirt, disgust, and disease: Is hygiene in our genes? Perspectives in biology and medicine, 44(1), 17–31.
Carroll JM, Russell JA (1996) Do facial expressions signal specific emotions? Judging emotion from the face in context. J Pers Soc Psychol 70: 205–218. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.70.2.205. PubMed: 8636880.
Dick, A.S., Goldin-Meadow,S., Hasson,U.,Skipper, J.I., & Small, S.L. (2009). Co- speech gestures influence neural activity in brain regions associated with processing semantic information. Human Brain Mapping, 30, 3509–3526.
Dolgin, K.G. and J. Sabini. Experimental manipulation of a human non-verbal display: The tongue-show affects an observer’s willingness to interact. Animal Behavior. 30(3): 935- 936.
Fusaro, M., Harris, P. L., & Pan, B. A. (2012). Head nodding and head shaking gestures in children’s early communication. First Language, 32, 439–458. doi:10.1177/0142723711419326
Fabbri-Destro, M.,& Rizzolatti,G. (2008). Mirror neurons and mirror systems in monkeys and humans. Physiology, 23, 171–179.
Fogassi, L., Gallese,V., Fadiga,L., & Rizzolatti,G. (1998). Neurons responding to the sight of goal directed hand/armactions in the parietal area PF (7b) of the macaque monkey. Society for Neuroscience, 24, 257.5.
Fusaro, M., Harris, P. L., & Pan, B. A. (2012). Head nodding and head shaking gestures in children’s early communication. First Language, 32, 439–458. doi:10.1177/0142723711419326
Gagnon, Mathieu ; Gosselin, Pierre ; Hudon-ven der Buhs, Isabelle ; Larocque, Karine ; Milliard, Karine. Children’s Recognition and Discrimination of Fear and Disgust Facial Expressions. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior. 2010. 34(1): 27-42.
Gentilucci, M., Bernardis, P., Crisi,G., & Dalla Volta, R. (2006). Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of Broca’s area affects verbal responses to gesture observation. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 18, 1059–1074.
Goldin-Meadow, S. (1999).The role of gesture in communication and thinking. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 3, 419–429.
Gräfenhain, M., Behne, T., Carpenter, M., & Tomasello, M. (2009). One-year-olds’ understanding of nonverbal gestures directed to a third person. Cognitive Development, 24, 23–33. doi:10.1016/j.cogdev.2008.10.001
Guidetti, M. (2005). Yes or no? How do young children combine gestures and words to agree and refuse. Journal of Child Language, 32, 911–924. doi:10.1017/S0305000905007038
Holle, H., & Gunter,T.C. (2007). The role of iconic gestures in speech disambiguation: ERP evidence. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19, 1175–1192.
Holler, J., Shovelton, H.,& Beattie, G.(2009).Do iconic hand gestures really contribute to the communication of semantic information in a face-to-face context? Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 33, 73–88.
Hubbard, A.L., Wilson, S. M., Callan, D. E., & Dapretto, M.(2009).Giving speech a hand: Gesture modulates activity in auditory cortex during speech perception. Human Brain Mapping, 30, 1028–1037.
He, Yifei ; Gebhardt, Helge ; Steines, Miriam ; Sammer, Gebhard ; Kircher, Tilo ; Nagels, Arne ; Straube, Benjamin. The EEG and fMRI signatures of neural integration: An investigation of meaningful gestures and corresponding speech. Neuropsychologia.. 2015. 72: 27-42.
Hansen, Jacqueline. Teaching without talking: teachers need to be aware of more than just the words they speak to children. They also need to monitor the nonverbal messages that they’re sending to students through proximity, eye contact, gestures, and touching. Phi Delta Kappan. 2010. 92(1): 35(6).
Inbar, Y., & Pizarro, D. Disgust, politics, and responses to threat [commentary]. The Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 2014. 37: 315-316.
Inbar, Y., Pizarro, D.A., Iyer, R., & Haidt, J. (2012). Disgust sensitivity, political conservatism, and voting. Social Psychological and Personality Science. 2012. 3: 537-544.
Inbar, Y., Pizarro, D.A., & Bloom Disgusting smells cause decreased liking of gay men. Emotion. 2012. 12: 23-27.
Inbar, Y., Pizarro, D.A., & Bloom, P. Conservatives are more easily disgusted than liberals. Cognition and Emotion. 2009. 23, 714-725.
Jones, N ; Kearins, J ; Watson, J. The human tongue show and observers’ willingness to interact: replication and extensions. Psychological reports. 1987. 60(3 Pt 1): 759-64.
http://www.amsciepub.com/doi/abs/10.2466/pr0.1987.60.3.759
Kunz, Miriam ; Peter, Jessica ; Huster, Sonja ; Lautenbacher, Stefan Gray, Marcus (Editor). Pain and Disgust: The Facial Signaling of Two Aversive Bodily Experiences (Comparing Facial Expressions of Pain and Disgust). 2013. 8(12): p.e83277
Kim, K. J. (1985). Development of the concept of truth-functional negation. Developmental Psychology, 21, 462–472. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.21.3.462
Katza, Carmit; Irit Hershkowitz; Lindsay C. Malloya; Michael E. Lamba; Armita Atabakia and Sabine Spindlera. Non-Verbal Behavior of Children Who Disclose or do not Disclose Child Abuse in Investigative Interviews. Child Abuse & Neglect. 2012. 36: 12-20.
http://bodylanguageproject.com/articles/reading-nonverbal-behaviour-child-abuse-cases-encourage-children-divulge-information-truth-telling/
Kendon,A.(1994).Do gestures communicate? A review. Research on Language and Social Interaction, 27, 175–200.
Knutson, K.M., McClellan,E.M., & Grafman, J.(2008).Observing social gestures: An fMRI study. Experimental Brain Research, 188, 187–198.
Kelly, S. D., Barr, D. J., Church, R. B., & Lynch, K.(1999).Offering a hand topragmatic understanding: The role of speech and gesture in comprehension and memory. Journal of Memory and Language, 40, 577–592.
Kelly, S. D., Creigh, P., & Bartolotti, J.(2009).Integrating speech and iconic gestures in a Stroop-like task: Evidence for automatic processing. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22, 683–694.
Kelly, S.D., Kravitz, C.,& Hopkins, M.(2004).Neural correlates of bimodal speech and gesture comprehension. Brain and Language, 89(1), 253–260.
Krahmer,E., & Swerts, M.(2007).The effects of visual beats on prosodic prominence: Acoustic analyses, auditory perception and visual perception. Journal of Memory and Language, 57, 396–414.
Krauss, R. M., Dushay, R.A., Chen,Y., & Rauscher, F.(1995).The communicative value of conversational hand gesture. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 31(6), 533–552.
Lindenberg, R., Uhlig,M., Scherfeld,D., Schlaug,G., & Seitz, R.J.(2012).Commu- nication with emblematic gestures: Shared and distinct neural correlates of expression and reception. Human Brain Mapping, 33, 812–823.
Moore, Monica. Courtship Signaling and Adolescents: Girls Just Wanna Have Fun. Journal of Sex Research. 1995. 32(4): 319-328.
http://bodylanguageproject.com/articles/girls-just-want-to-have-fun-the-origins-of-courtship-cues-in-girls-and-women/
Navarro, Joe. 2008. What Every BODY is Saying: An Ex-FBI Agent’s Guide to Speed-Reading People. William Morrow Paperbacks.
Negriff, Sonya ; Noll, Jennie G ; Shenk, Chad E ; Putnam, Frank W ; Trickett, Penelope K. Associations between nonverbal behaviors and subsequent sexual attitudes and behaviors of sexually abused and comparison girls. Child maltreatment. 2010. 15(2): 180-9.
Ohgami, Y., Matsuo,K., Uchida,N., & Nakai,T. (2004). An fMRI study of tool-use gestures: Body partas object and pantomime. Neuroreport, 15, 1903–1906.
Pizarro, D.A., Inbar, Y., and Helion, C.. On disgust and moral judgment. Emotion Revie2. 2011. 3: 267–268.
Skipper, J.I., Goldin-Meadow, S., Nusbaum,H.C.,& Small,S.L. (2007).Speech- associated gestures, Broca’s area, and the human mirror system. Brain and Language, 101, 260–277.
Sherzer, Joel The Brazilian Thumbs-Up Gesture. Journal of Linguistic Anthropology, 1991, Vol.1(2), pp.189-197
Straube,B., Green,A., Bromberger,B., & Kircher, T. (2011).The differentiation of iconic and metaphoric gestures: Common and unique integration processes. Human Brain Mapping, 32, 520–533.
Straube, Benjamin ; Green, Antonia ; Jansen, Andreas ; Chatterjee, Anjan ; Kircher, Tilo. Social cues, mentalizing and the neural processing of speech accompanied by gestures. Neuropsychologia. 2010. 48(2): 382-393.
Schnall, S., Haidt, J., Clore, G. L., & Jordan, A. H. (2008). Disgust as embodied moral judgment. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 34, 1096–1109. doi:10.1177/0146167208317771.
Smith, John, Julia Chase, and Anna Lieblich (1974). “Tongue Showing.” In Semiotica (Vol. 11, No. 3), pp. 201-46.
Stern, Daniel and Estelle Bender (1974). “An Ethological Study of Children Approaching a Strange Adult.” In Richard Friedman et al. (Eds.), Sex Differences in Behavior (New York: John Wiley and Sons), pp. 233-58.
Tam, C. W., & Stokes, S. F. (2001). Form and function of negation in early developmental Cantonese. Journal of Child Language, 28, 373–391. doi:10.1017/S0305000901004688
Underwood, M. K.. Glares of Contempt, Eye Rolls of Disgust and Turning Away to Exclude: Non-Verbal Forms of Social Aggression among Girls. Feminism & Psychology. 2004 14(3): 371-375
Villarreal, M., Fridman,E.A., Amengual,A., Falasco,G., Gerscovich,E.R., Ulloa,E.R., et al. (2008). The neural substrate of gesture recognition. Neuropsychologia, 46, 2371–2382.
Vaidyanathan, R. (1991). Development of forms and functions of negation in the early. tages of language acquisition: A study in Tamil. Journal of Child Language, 18, 51–66. doi:10.1017/S0305000900013295
Willems, R.M., Ozyurek,A., & Hagoort,P.(2007).When language meets action:The neural integration of gesture and speech. CerebralCortex, 17, 2322–2333.
Wieser, Matthias J.; Tobias Flaisch and Paul Pauli. Raised Middle-Finger: Electrocortical Correlates of Social Conditioning with Nonverbal Affective Gestures. 2014. PLoS ONE 9(7): e102937. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0102937
http://bodylanguageproject.com/articles/powerful-nonverbal-effect-raised-middle-finger-persistent-brain-consequences-pairing/
Wu, Y. C., & Coulson, S.(2005).Meaningful gestures: Electrophysiological indices of iconic gesture comprehension. Psychophysiology, 42, 654–667.
Wolf K, Mass R, Ingenbleek T, Kiefer F, Naber D et al. (2005) The facial pattern of disgust, appetence, excited joy and relaxed joy: an improved facial EMG study. Scand J Psychol 46: 403-409. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9450.2005.00471.x. PubMed: 16179022.
Xu,J., Gannon,P.J., Emmorey,K., Smith,J.F., & Braun,A.(2009). Symbolic gestures and spoken language are processed by a common neural system. Proceedings of the NationalAcademyofSciences, 106, 20664–20669.
Zeinstra, Gertrude G.; M.A. Koelen; D. Colindres ; F.J. Kok; C de Graaf. Facial Expressions in School-Aged Children are a Good Indicator of ‘Dislikes’, but not of ‘Likes.’ Food Quality and Preference. 2009. 20: 620-624.
http://bodylanguageproject.com/articles/read-kids-dislike-food-facial-expressions-accurate-detecting-dislike-not-like-children/