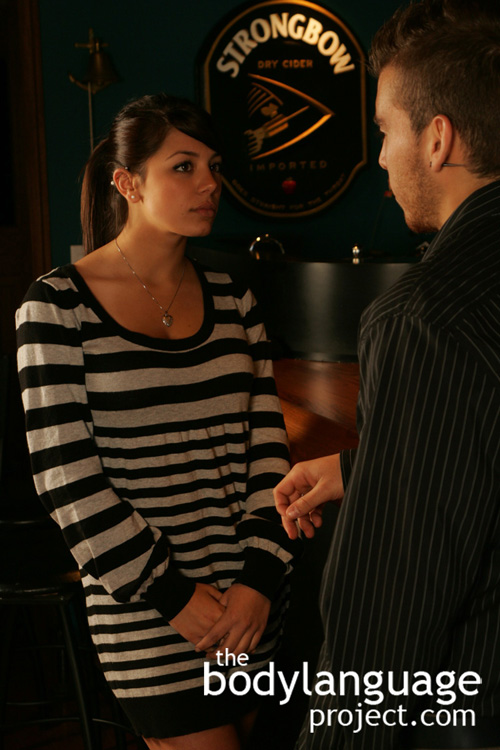
Emotional body language is a charged topic because it essentially defines people. When we talk about emotions we talk about what motivates people which includes but is certainly not limited to fear, anger, sadness, timidity or shyness, disgust, and happiness. Emotional nonverbal communication is present everyday, and in many forms, and can reduce conflict before it starts, or identify weaknesses that can be soothed or taken advantage of, depending on the particular desires of the body language reader. Before dispelling outright the desire to exploit, remind yourself that in most cases, there exists some degree of competition or cooperation in all of life, which is frequently only differentiated by matters of degree, type and more importantly, outcome. Thus, if one wishes to formulate mutual agreements through cooperation, or feels compelled to assist those who are at a disadvantage, they should welcome and read the body language just the same. In other words, read emotions to discover underlying insecurities or happiness in other people and do with it as you please, but also be aware of your own signals since it will give ammunition to others that can be used against you. Sometimes these cues end up in the less that charitable people around you such as predators. This makes knowing the cues important in displaying victim type body language to avoid appearing like an easy target, and not just to criminals, but to salesman, potentially abusive spouses, and children looking to take advantage of our goodwill.
In this chapter we will cover many topics including displacement behaviour which includes any nonverbal signal meant to quell anxiety due to encroachment on personal space. As we learned previously, personal space and territories play an important function in our lives, however, these zones are frequently breeched when in busy city streets and other public areas. We also cover how the fight or flight mechanism plays into body language and how the catch phrase is a misnomer because animals and people don’t usually respond in that way, at least not in that order. Clenching and gripping body language is also covered. We’ll see how the aforementioned is an important subset of body language since it reveals inner tension and how, and perhaps more importantly, why, nervous hands shake and what it all means to poker players. We will even discover what sort of body language indicates that a person has a poor self image, the role eyebrows play with respect to the emotions they convey, what interlaced fingers that rub together and palm finger stroking mean, and how suckling and mouthing turns us back into babies. Next we cover why compressed lips and lip pursing aren’t the same, nor do they mean that someone wants to kiss. In fact, coupled with the down-turned smile they all mean negative thoughts are being passed around in the mind.
This chapter also covers a smorgasbord of other emotionally charged cues such as how tongues show concentration and cheekiness, the sneering of the nose, what ear grabbing means and hostile body language in brief, since it was extensively covered previously, and how rejection takes place in sequence so we can run when we see it, or emit it when we wish to repeal the boring! If rejecting is too pessimistic for you, what follows is how relaxation is made evident through body language. Neck and nose body language is hit on next which become particularly sensitive under pressure and tends to require frequent touching or covering so as to produce feelings of comfort through protection. Blocking is also dealt with which can happen through various forms, such as the body or eyes, but each have roots in the fight or flight response. We hit on the colour of emotion including blushing and blanching, as well as gravity defying body language found when people experience joyful exuberance. The six main facial expressions which are happiness, sadness, surprise, fear, anger and disgust are cataloged and described leading into whether or not emotions can easily be faked. We also learn in this chapter that people will take “emotional downtime” frequently throughout the day, laypeople call this “daydreaming.” Cocooning and turtling body positions are described which both point to insecurity and timidity as roots. We’ll also cover how we can tell if people are related or having intimate relations based on how they hug and conclude with the remaining emotional body language.