Body Language of The Ear Grab
 Cue: Ear Grab
Cue: Ear Grab
Synonym(s): Ear Rub, Ear Rubbing, Grabbing The Ear, Touching The Ear, Pulling At The Ear, Ear Pull, Ear Touch, Hand To Ear.
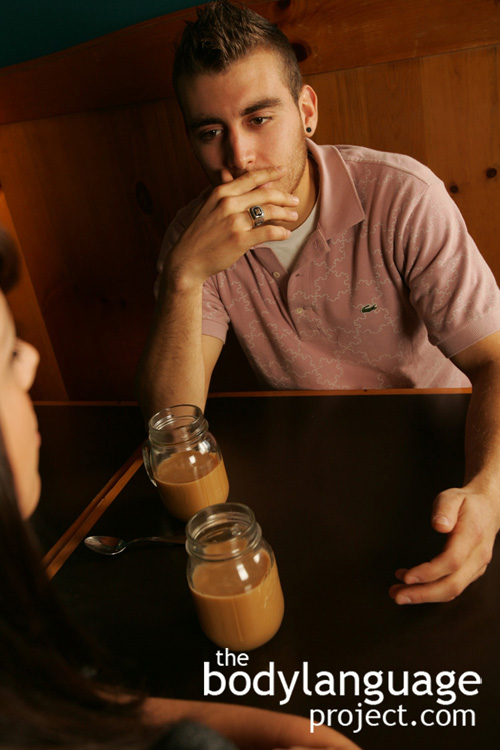
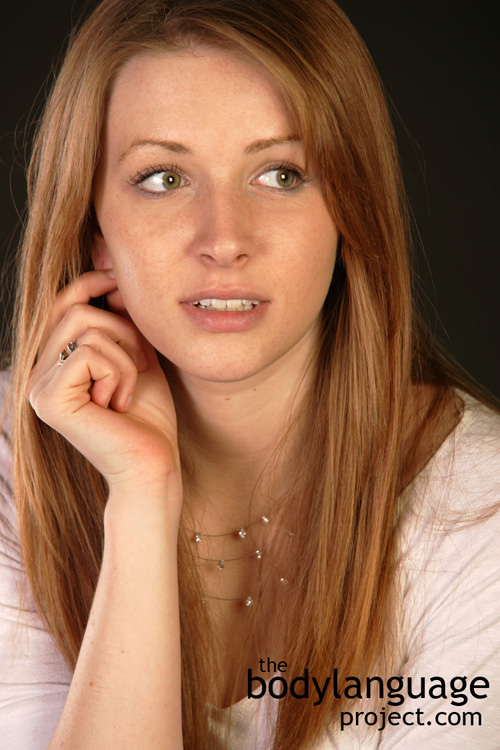
Description: The hand reaches up and grabs, scratches, tugs, or lightly touches or partially covers the ear. If an earring is being worn, a person might roll or tug it instead. In more overt ear language, a person might cover their ears completely, which is usual in children who haven’t yet learned to how to minimize the gesture.
In One Sentence: Grabbing the ear is attributed to those experiencing visceral stress but usually simply serves to alleviate an itch.
How To Use it: Touching parts of the face is not advisable as it generally comes across as negative. Do avoid touching the face as much as possible including the ears when trying to appear open and honest.
Context: a), b), c) General.
Verbal Translation: a) “I’m touching my ear because what I’m hearing is causing me stress and touching my ear helps to relieve it.” b) “I can’t believe what I’m hearing.” c) “This is causing me emotional discomfort and which is making my ears flush. To fix the discomfort, I feel like tugging at my ear.”
Variant: See Hand To Nose, Neck Rubbing (back of neck) or Holding The Back Of The Neck.
Cue In Action: a) During court proceedings, a witness began to delve deeper into the case. The defendant didn’t like what she was hearing and she began to flush in the ears causing her to tug at her ears. A used car salesman might talk about the quality of a certain car, then pull on his ear lobe, or more subtly, he might be found rubbing the edge of the ear, indicating that what he has just said is untrue.
Meaning and/or Motivation: The ear grab refers to a subconscious desire to “hear no evil” and is done by reaching up and pulling the ear in response to hearing or saying discomforting things. It also sometimes represents anxiety and nervousness.
Think of the ear grab like rubbing sore muscles or massaging a stiff back, except in this case the damage done is internal and it’s due to something that has been heard, which “hurts” the ears. Anytime someone shows the desire to touch their ear means that they are thinking about hearing, and it will be up to you to tie them to context and decide what it is they are really saying. Other times, the ear is scratched because it really is itchy and has no meaning at all (an adaptor).
The ear grab can be use not only at the conclusion of the lies of others, but also at the conclusion of our own lies as well. The gesture used at the conclusion of our own lies serves to reduce what is called “cognitive dissonance” which is the uncomfortable feeling that comes from holding two contradictory ideas simultaneously.
Cue Cluster: In order for the ear tug to have any true meaning of discomfort other cues must be present such as blushing, touching the face or neck, submissive cues, eye aversion or eyes shifting, head lowered, feet turning away, hands and feet freezing, rubbing the hands on the thighs, rubbing the back of the head or neck, massaging the throat or covering the neck dimple and so forth.
Body Language Category: Adaptors, Auto contact or self touching, Defensive, Displacement behaviour, Doubt or disbelief body language, Embarrassment (nonverbal), Pacifying, Lying or deceptive body language, Negative body language, Shy nonverbal.
Resources:
Akehurst, L., G. Kohnken, A. Vrij, and R. Bull. 1996. Lay persons’ and police officers’
beliefs regarding deceptive behaviour. Applied Cognitive Psychology 10: 461-471.
Appelbaum, P.S. The new lie detectors: Neuroscience, deception, and the courts. Psychiatric Services. 2007. 58: 460-462.
Barroso, Felix ; Feld, Jason. Self-touching and attentional processes: The role of task difficulty, selection stage, and sex differences. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior. 1986. 10(1): 51-64.
Butzen, Nathan David ; Bissonnette, Victor ; Mcbrayer, Dan. Effects of modeling and topic stimulus on self-referent touching. Perceptual and motor skills. 2005. 101(2): 413-20.
Broome, Marion E.. Helping Parents Support Their Child In Pain. Pediatric Nursing. 2000. 26(3): 315.
Bornstein, Marc H. ; Tamis-Lemonda, Catherine S. Maternal responsiveness and infant mental abilities: Specific predictive relations. Infant Behavior and Development. 1997. 20(3): 283-296.
Buckley, V., & Semple, S. (2012). Evidence that displacement activities facilitate behavioural transitions in ring-tailed lemurs. Behavioural Processes, 90, 433–435.
Bernal, Gilda Rios ; Wortham, Suec. How to Calm Children through Massage. Childhood Education. 1997. 74(1): 9-14.
Bouhuys, A.L. ; Jansen, C.J. ; van den Hoofdakker, R.H. Analysis of observed behaviors displayed by depressed patients during a clinical interview: relationships between behavioral factors and clinical concepts of activation. Journal of Affective Disorders. 1991. 21(2): 79-88.
Bouhuys, A.L. ; Beersma, Domien G.M. ; van den Hoofdakker, Rutger H. Observed behavior as a predictor of the response to sleep deprivation in depressed patients. Psychiatry Research. 1989. 28(1): 47-61.
Berridge CW,Mitton E, ClarkW, Roth RH. 1999. Engagement in a non-escape (displacement) behavior elicits a selective and lateralized suppression of frontal cortical dopaminergic utilization in stress. Synapse 32:187–197.
Bond, Michael H., and Hiroshi Komai (1976). “Targets of Gazing and Eye Contact During Interviews: Effects on Japanese Nonverbal Behavior.” In Journal of Personality and Social Psychology (Vol. 34), pp. 1276-84.
Blakeslee, Sandra (1995). “In Brain’s Early Growth, Timetable Maybe Crucial.” In New York Times (“Science Times,” August 29), pp. C1, C3.
Caso, L., A. Gnisci, A. Vrij, and S. Mann. 2005. Processes underlying deception: an empirical analysis of truth and lies when manipulating the stakes. Journal of Investigative Psychology and Offender Profiling 2 (3): 195-202.
Caplovitz Barrett, Karen. The origins of social emotions and self-regulation in toddlerhood: New evidence. Cognition & Emotion. 2005. 19(7): 953-979.
Castles, Duncan L. ; Whiten, Andrew ; Aureli, Filippo. Social anxiety, relationships and self-directed behaviour among wild female olive baboons. Animal Behaviour. 1999. 58(6): 1207-1215.
Charles v. Ford, Lies! Lies! Lies!: The Psychology of Deceit (Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Press, Inc., 1996), 200.
Dimond, Stuart ; Harries, Rashida. Face touching in monkeys, apes and man: Evolutionary origins and cerebral asymmetry. Neuropsychologia. 1984. 22(2): 227-233.
D’alessio, M. ; Zazzetta, A. Development of Self-Touching Behavior in Childhood. Perceptual and Motor Skills. 1986. 63(1): 243-253.
DeSteno, D.; Breazeal, C.; Frank, R. H.; Pizarro, D.; Baumann, J.; Dickens, L, and Lee, J. Detecting the Trustworthiness of Novel Partners in Economic Exchange. Psychological Science. 2012. 23, 1549-1556.
http://bodylanguageproject.com/articles/use-body-language-cues-create-trust
Elaad, E. 2003. Effects of feedback on the overestimated capacity to detect lies and the underestimated ability to tell lies. Applied Cognitive Psychology 17(3): 349-363.
Edelstein, R. S., T. L. Luten, P. Ekman, and G. S. Goodman. 2006. Detecting lies in children and adults. Law and Human Behavior 30(1): 1-10.
Ekman, Paul, and Wallace V. Friesen (1969). “Nonverbal Leakage and Clues to Deception.” In Psychiatry (Vol. 32), pp. 88-106.
Frank M.G. and Ekman P. 1997. The ability to detect deceit generalizes across different types of high-stake lies. Source: Journal of personality and social psychology. 72: 1429 -39
Gordon, A. K. and A. G. Miller. 2000. Perspective differences in the construal of lies: is deception in the eye of the beholder? Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 26 (1): 46-55.
Goldberg, Shelly ; Rosenthal, Robert. Self-touching behavior in the job interview: Antecedents and consequences. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior. 1986. 10(1): 65-80.
Goodall, Jane (1986). The Chimpanzees of Gombe: Patterns of Behavior (Cambridge: Belknap Press of Harvard University).
Givens, David B. (1976). An Ethological Approach to the Study of Human Nonverbal Communication (University of Washington Ph.D. dissertation in Anthropology, Ann Arbor: University Microfilms).
Grand, Stanley (1977). “On Hand Movements During Speech: Studies of the Role of Self-Stimulation in Communication Under Conditions of Psychopathology, Sensory Deficit, and Bilingualism.” In Norbert Freedman and Stanley Grand, eds., Communicative Structures and Psychic Structures: A Psycholanalytic Interpretation of Communication (New York: Plenum Press), pp. 199-221.
Hernandez-Reif, Maria ; Diego, Miguel ; Field, Tiffany. Preterm infants show reduced stress behaviors and activity after 5 days of massage therapy. Infant Behavior and Development. 2007. 30(4): 557-561.
Harrison, Lynda Law. The use of comforting touch and massage to reduce stress for preterm infants in the neonatal intensive care unit. Newborn and Infant Nursing Reviews. 2001. 1(4): 235-241.
Hennessy, Michael B ; T. Williams, Michael ; Miller, Deborah D ; Douglas, Chet W ; Voith, Victoria L. Influence of male and female petters on plasma cortisol and behaviour: can human interaction reduce the stress of dogs in a public animal shelter?
Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 1998. 61(1): 63-77.
Harrigan, Jinni A. Self-touching as an indicator of underlying affect and language processes. Social Science & Medicine. 1985. 20(11): 1161-1168.
Harrigan, Jinni A.; Karen S. Lucic; Denise Kay; Anne McLaney and Robert Rosenthal. Effect of Expresser Role and Type of Self-Touching on Observers’ Perceptions. Journal of Applied Social Psychology. 1991. 21(7): 585-609.
Heaven, Laura ; Mcbrayer, Dan ; Prince, Bob. Role of sex in externally motivated self-touching gestures. Perceptual and motor skills. 2002. 95(1): 289-94.
Heaven, L ; Mcbrayer, D. External motivators of self-touching behavior. Perceptual and motor skills. 2000. 90(1): 338-42.
Kammers, Marjolein P.M. ; de Vignemont, Frédérique ; Haggard, Patrick. Cooling the Thermal Grill Illusion through Self-Touch. Current Biology. 2010. 20(20): 1819-182.
Katza, Carmit; Irit Hershkowitz; Lindsay C. Malloya; Michael E. Lamba; Armita Atabakia and Sabine Spindlera. Non-Verbal Behavior of Children Who Disclose or do not Disclose Child Abuse in Investigative Interviews. Child Abuse & Neglect. 2012. 36: 12-20.
http://bodylanguageproject.com/articles/reading-nonverbal-behaviour-child-abuse-cases-encourage-children-divulge-information-truth-telling
Karagozoglu, Serife ; Kahve, Emine. Effects of back massage on chemotherapy-related fatigue and anxiety: Supportive care and therapeutic touch in cancer nursing. Applied Nursing Research. 2013. 26(4): 210-217.
Kossowsky, Joe ; Wilhelm, Frank H. ; Schneider, Silvia. Responses to voluntary hyperventilation in children with separation anxiety disorder: Implications for the link to panic disorder. Journal of Anxiety Disorders. 2013. 27(7): 627-634.
Kochanska, G., Coy, K. C., & Murray, K. T. (2001). The development of self-regulation in the first four years of life. Child Development, 72, 1091–1111.
Kochanska, G., Murray, K. T., & Harlan, E. T. (2000). Effortful control in early childhood: Continuity and change, antecedents, and implications for social development. Developmental Psychology, 36, 220–232.
Kenner, Andrew N. (1993). “A Cross-Cultural Study of Body-Focused Hand Movement.” In Journal of Nonverbal Behavior (Vol. 17, No. 4, Winter), pp. 263-79.
Lee Ann Renninger, T. Joel Wade, Karl Grammer. Getting that female glance: Patterns and consequences of male nonverbal behavior in courtship contexts. Evolution and Human Behavior. 2004; 25: 416–431.
http://bodylanguageproject.com/articles/part-i-how-to-read-male-sexual-body-language-a-study-for-women-and-the-men-who-wish-to-cheat-the-system/
Mann, S., A. Vrij, and R. Bull. 2002. Suspects, lies, and videotape: an analysis of authentic high-stake liars. Law and Human Behavior 26 (3): 365-376.
Mann, S., A. Vrij, and R. Bull. 2004. Detecting true lies: police officers’ ability to detect suspects’ lies. Journal of Applied Psychology 89(1): 137-149.
Moszkowski, Robin J. ; Stack, Dale M. ; Chiarella, Sabrina S. Infant touch with gaze and affective behaviors during mother–infant still-face interactions: Co-occurrence and functions of touch. Infant Behavior and Development. 2009. 32(4): 392-403.
Maestripieri D, Schino G, Aureli F, Troisi A. 1992. A modest proposal: displacement activities as an indicator of emotions in primates. Anim Behav 44:967–979.
Mohiyeddini, C., Bauer, S., & Semple, S. (2013a). Displacement behaviour is associated with reduced stress levels among men but not women. PLoS One, 8, e56355.
Mohiyeddini, C., Bauer, S., & Semple, S. (2013b). Public self-consciousness moderates the link between displacement behaviour and experience of stress in women. Stress, 16, 384–392.
Mohiyeddini, C., & Semple, S. (2013). Displacement behaviour regulates the experience of stress in men. Stress, 16, 163–171.
Marcus-Newhall A, Pedersen WC, Carlson M, Miller N. 2000. Displaced aggression is alive and well: a meta-analytic review. J Pers Soc Psychol 78:670–689. Ingram GIC. 1960. Displacement activity in human behavior. Am Anthropol. 62:994–1003.
Morris, Desmond (1994). Bodytalk: The Meaning of Human Gestures (New York: Crown Publishers).
McGrew, W. C. (1972). “Aspects of Social Development in Nursery School Children with Emphasis on Introduction to the Group.” In N. G. Blurton Jones, ed., Ethological Studies of Child Behaviour (Cambridge: University Press), pp. 129-56.
Navarro, Joe. 2008. What Every BODY is Saying: An Ex-FBI Agent’s Guide to Speed-Reading People. William Morrow Paperbacks.
Pease, Barbara and Allan Pease. 2006. The Definitive Book of Body Language Hardcover. Bantam.
Park, H. S., T. R. Levine, S. A. McCornack, K. Morrison, and M. Ferrara. How people really detect lies. Communication Monographs. 2002. 69: 144-157.
Pecora, Giulia ; Addessi, Elsa ; Schino, Gabriele ; Bellagamba, Francesca. Do displacement activities help preschool children to inhibit a forbidden action? Journal of Experimental Child Psychology. 2014. 126: 80-90.
Pugh, George E. (1977). The Biological Origin of Human Values (New York: Basic Books).
Rosenfeld, Howard (1973). “Nonverbal Reciprocation of Approval: An Experimental Analysis.” In Argyle *, pp. 163-72.
Sommer, Robert (1969). Personal Space: The Behavioral Basis of Design (Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall).
Stromwell, L. A., P. A. Granhag, and S. Landstrom. 2007. Children’s prepared and unprepared lies: can adults see through their strategies? Applied Cognitive Psychology 21 (4): 457-471.
Schaafsma, Juliette ; Krahmer, Emiel ; Postma, Marie ; Swerts, Marc ; Balsters, Martijn ; Vingerhoets, Ad. Comfortably Numb? Nonverbal Reactions to Social Exclusion. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior. 2015. 39(1): 25-39.
Schino G, Perretta G, Taglioni AM, Monaco V, Troisi A. 1996. Primate displacement activities as an ethopharmacological model of anxiety. Anxiety 2:186–191.
Supplee, Lauren H ; Skuban, Emily Moye ; Shaw, Daniel S ; Prout, Joanna. Emotion regulation strategies and later externalizing behavior among European American and African American children. Development and Psychopathology. 2009. 21(2): 393-415.
Troisi A (2002) Displacement activities as a behavioural measure of stress in nonhuman primates and human subjects. Stress 5: 47–54.
Troisi A (1999) Ethological research in clinical psychiatry: the study of nonverbal
behaviour during interviews. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23: 905–913.
Troisi A, Moles A (1999) Gender differences in depression: an ethological study
of nonverbal behaviour during interviews. J Psychiatr Res 33: 243–250.
Vrij, A. and G. R. Semin. 1996. Lie experts’ beliefs about nonverbal indicators of
deception. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior 20: 65-80.
Vrij, A. 1997. Individual differences in hand movements during deception. Source: Journal of nonverbal behavior. 21: 87-102.
Vrij, A.. 2004. Why professionals fail to catch liars and how they can improve Source: Legal and Criminological Psychology. 9:159-181.
Vrij, A., S. Mann, and S. Kristen. 2007. Cues to deception and ability to detect lies as a function of police interview styles. Law and Human Behavior 31 (5): 499-518.
von Hippel W, von Hippel C, Conway L, Preacher KJ, Schooler JW, et al. (2005) Coping with stereotype threat: denial as an impression management strategy. J Personal Soc Psychol 89: 22–35.