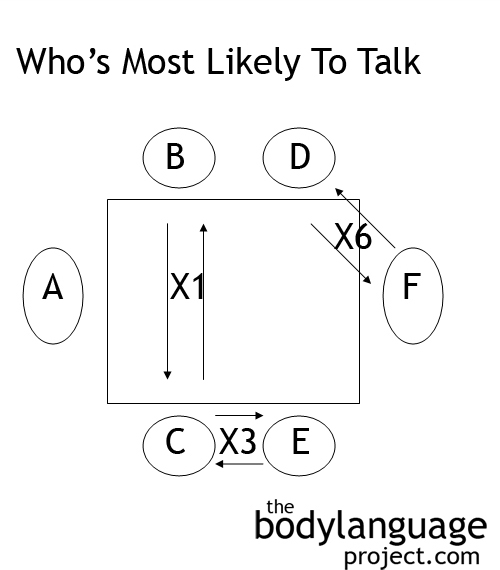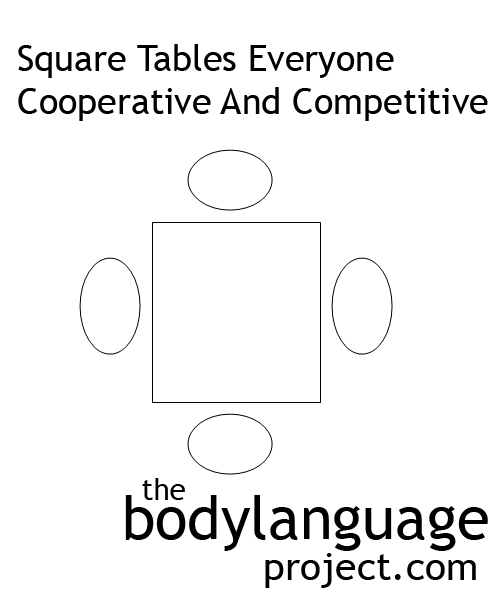
In a square table seating arrangement, each person is in a competitive (head-to-head) position and a cooperative (kitty-corner) position. This can present an interesting situation.
Square tables present an interesting situation. If we draw on what we know about rectangular tables we know that people who sit face-to-face are in a competitive position and those to our rights and lefts are in cooperative positions. Thus, everyone is equally competing and cooperating with someone at the table completely leveling the playing field. Square tables are great for quick meetings because of this dichotomy.
Bridge is an interesting game played on a square table. In the game there are four players in two fixed partnerships. The partners sit facing each other. It is the tradition to name the players according to their position at the table. They are called North, East, South and West. North and South are partners playing against East and West. In this card game, partners are not allowed to convey information to each other by talking, gestures or facial expression. The intent of the game is to exchange information by the choice of bids or cards played, but how well does this bode with the information we know about seating arrangements? The game has done well to prevent partners sitting next to each other preventing close quarter exchanges that might go unnoticed. However, it does allow partners to face each other head-on exposing their full fronts to each other and also prevents opponents from gaining the same view. While partners aren’t permitted to use any language whatsoever to exchange cues, being students of body language and aware of it’s proficient and pervasiveness might expect something different from the game whether or not it’s ever detected. Naturally, you’ll draw your own conclusions!