Seating arrangements is one of the things we infrequently draw to conscious attention but at some level always understand its importance. In this chapter we looked at what seems on the outset to be a complicated matter, but in reality is fairly straight forward and like all body language, once it is know, common sense. We found that seating positions can indicate our reason for meeting, be it ‘affiliation’ – to build group cohesion, ‘achievement’ – to get things done, or ‘power’ – to emphasis control. We found that the meeting organizer typically dictates how meetings will transpire.
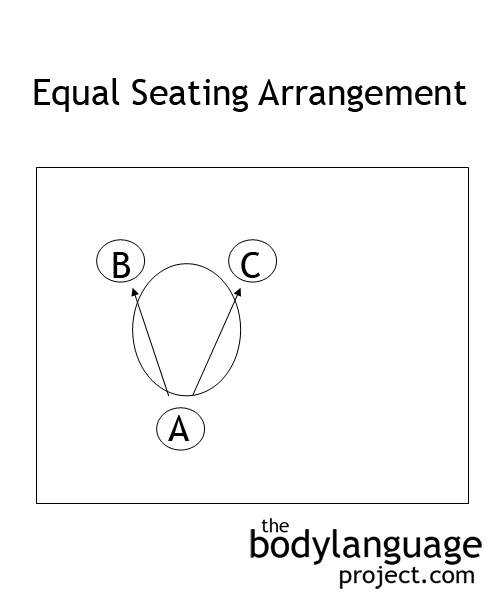
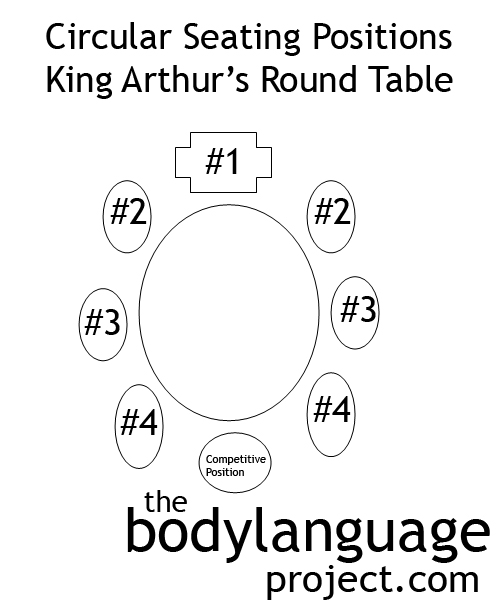
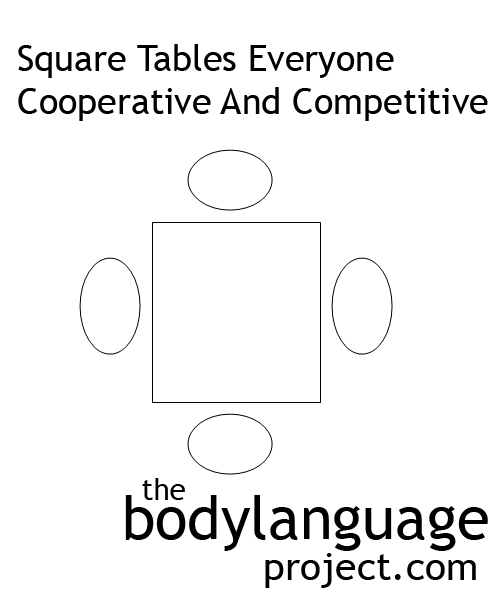
We learned that Sommer first began researching seating ecology and that patterns emerged based on the shape of the table and the proximity speakers had to one-another. We found that a casual corner position where speakers meet across the corners of a rectangular or square table preserve closeness between people, but still offers the security of a partial barrier. We found that when seated side-by-side cooperation is fostered, when facing across from one-another but not head-on, independent though is fostered, and when facing directly, competition. We found that leadership studies show us what we intuitively already know, that leaders take up the head position, that those at his or her flank receive trickle down leadership and that when seating is pre-determined, leadership is assigned to the head of the table. We found that square tables includes both competitive and cooperative seating positions, that circular tables had similar affects despite what King Arthur thought, and that strategically we can sway our “object” by taking up competitive and affiliative positions.
Next we looking at how to set up an office and found that desk placement and office artifacts are crucial and that chairs can make people uncomfortable or powerful depending on their height and location. We then looked at seating arrangements in larger auditoriums and saw that the center of lecture halls tended to be overlooked, and also how to use this to our advantage, and finally we concluded the chapter by pointing out that seating location affects participation; those in front participating most, but that it did not related to test scores.