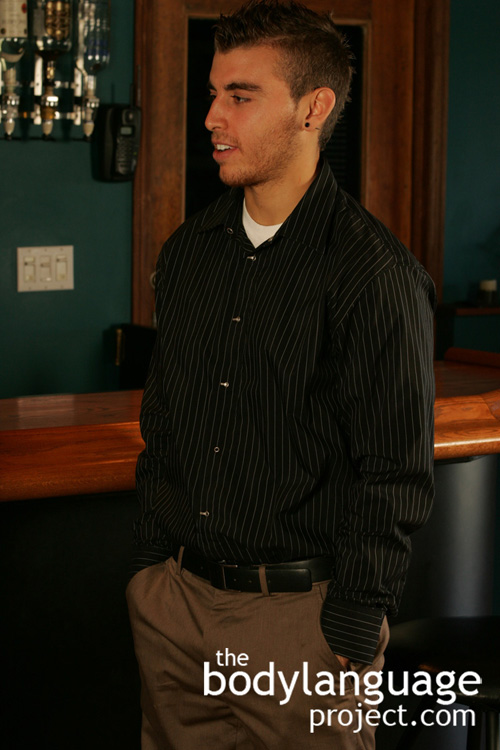
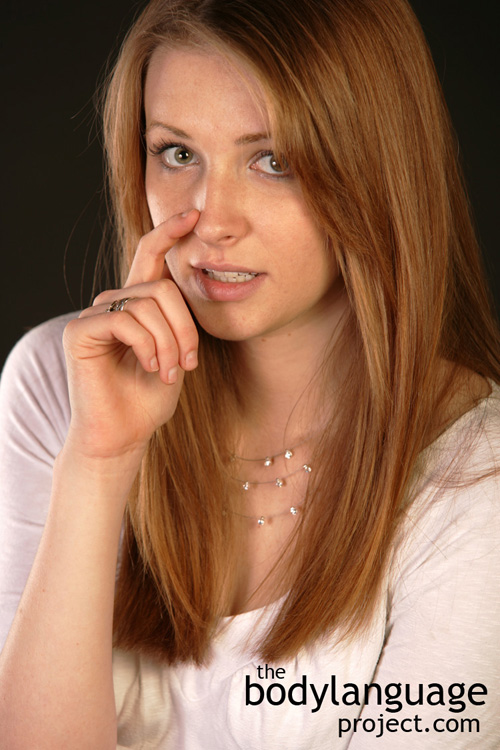
By now we know that liars are practiced, we all do it, and we do it regularly. Sometimes we don’t even realize we do it and other times those around us don’t care to know. What we do know is that most liars feel only mild feelings of guilt and fear. Thus, we should only expect very subtle clues to deception and nothing more. It has been shown through the research that looking for full blown signals of lying is both misleading and even unhelpful. Liars as it were, are only slightly more apprehensive than truth tellers with both feeling nervous and anxious when faced with scrutiny.
My advice to read people is to watch for the little stuff, the microexpressions, the small gestures and the ones that happen instantly, and then hone in on it. Keep in mind too, that you won’t be able to detect lies much better than about seventy-five percent of the time anyway, which is on par with the CIA minus of course various lie detection machines which we discussed as being impractical and requiring cooperation that you are very unlikely to garner, even if provided with access.
The top lie detectors all seem to have one trait in common, and that is skepticism. They know or assume that someone is lying so they view them through that window being careful to watch and recall any cues that tip the scales toward deception. Looking at the world through rose-coloured glasses will lead to rose-coloured predictions about people and this is all just dandy, if you aren’t interesting in uncovering bad things around you. You also must be aware of a person, from their face to their toes and be willing to look them over and actively observe them. If you’re goal is to make friends, then by all means avoid filtering and analyzing the body language around you. In fact, I would advise body language readers to relax their skills when around family and friends, or at least keep it secret!
It is not safe to immediately peg someone a liar based on one or even a handful of cues just by the nature of the trade. Reading lying correctly is a long term comparison of the facts seeded with emotional, fearful and stressed body language from one moment to the next that can only happen over time. Success will come by looking at the full picture and comparing the parts to the whole and digging deeper when discrepancies happen between expressive behaviours and the words said. No doubt, lie detection is difficult, but the body language in this chapter coupled with how it is framed, that is the lie detection theory and it’s limitations, will help increase your odds significantly.