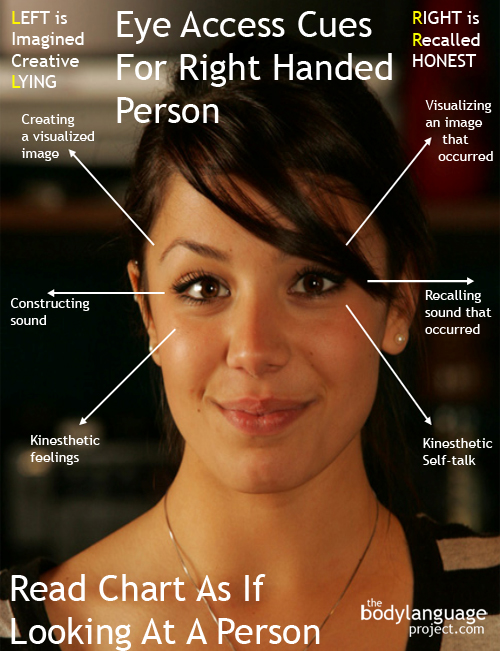
To apply the psychic NLP eye trick examine where people look as they attempt to recollect or express their thoughts. For most right-handed people, eye movement up and to the left is a signal that one is accessing a visual memory whereas movement up and right means that a person is trying to construct a visual image. Eyes either right or left, but still level, indicate an auditory process such as remembering sounds and words. Eyes down and left indicate internal dialogue or self talk, and down and right indicate a tactile or visceral feeling. When the eyes are straight ahead, unfocused or dilated, they signal that visual or sensory information is being accessed.
These eye patterns appear to be consistent for all right handed people throughout the world except for a few minor exceptions. Many left handed people though tend to reverse from left to right and access information opposite to right handed people. Therefore, they tend to look down and left to access feelings instead of up and left.
These patterns can provide us with information that have predictive powers. By watching and reading the eye direction of other people we can draw inferences about how they are accessing the information which can be particularly helpful when trying to determine their intentions. Lie detection comes first to mind, but we can also deduce how one is internalizing thought by what their eyes are doing. As it pertains to lying, for example, right and up (constructed visual) and right and level (constructed auditory) both show that a person is trying to create or imagine new details about something whereas left and up (visual remembered) and left and level (auditory remembered) indicating that a person is remembering something that had actually happened.
A word of caution though is that it is not all that easy to follow someone’s eyes and some of the expressions last just fractions of seconds. Not only this, but people can access multiple parts of their brain to recall the similar ideas. Some people also have habitual eye movements that have developed over time so a person that is highly visual might look up and left, or right, regardless of the type of question being asked. Someone who is kinesthetically oriented might look down and right all the time even in reference to a thought about music or sound. However, even these cues can give us indications of the
types of mind they have and therefore the type of person they are. By using eye gaze in NLP we can better tailor presentations to key in on more visual or auditory elements as required by our listeners.
Here is a list of questions to help determine what type of learner you are working with in order to better help you tailor information:
1) Visual Remembered: Think of the colour of your first bicycle. Think of the first person you saw as you entered the office this morning.
2) Visual Construction: Imagine what it would be like to fly. Imagine your dream home and pretend you are entering through the front door, what do you see?
3) Auditory Remembered: What was one of your most favourite things your parents have ever said to you? What types of sounds do you most enjoy?
4) Auditory Constructed: What would a rabbit sound like it if could talk? What would your boss say if he knew you were stealing office supplies?
5) Auditory Digital (Internal Self Talk): What does the sound of your inner voice make? What kind of dialogue happens when you think of your spouse and children? When do you find you talk to yourself the most?
6) Kinesthetic Remembered (Tactile and Emotional): Imagine what sandpaper feels like against your skin. Imagine what a cat feels like as you pet it. Think of a time in your life when you felt you had accomplished something that made you proud. When was the last time you were completely exhausted?
7) Kinesthetic Construction (Tactile and Emotional): Imagine the feeling of sand between your fingers that gradually turned sticky instead of rough. Imagine the feeling of helplessness turned into empowerment.