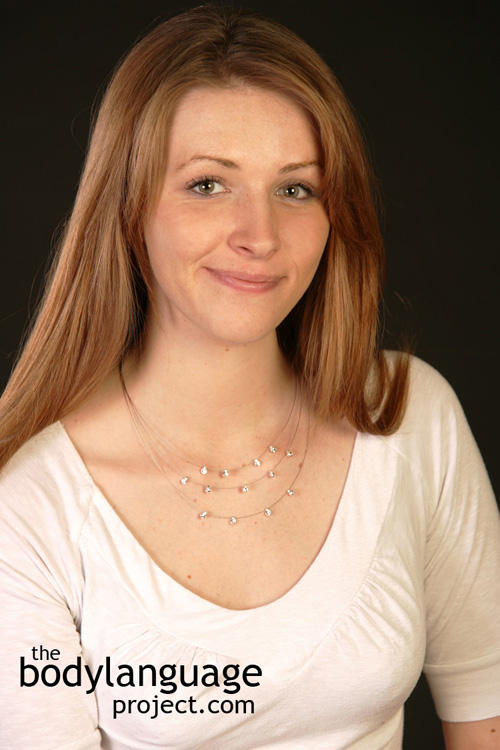
Keep in mind that microexpressions are useful when they appear out of congruency with other gestures or language. It is when the facial expression is out of tune with what is being said. For example, telling a positive story while smiling and momentarily flashing a microexpression can mean that the person is lying. Here are some microexpressions with respect to emotions. [note that images show true expressions which might be held for a time, whereas a microexpression will not persist, only flash quickly before disappearing]
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
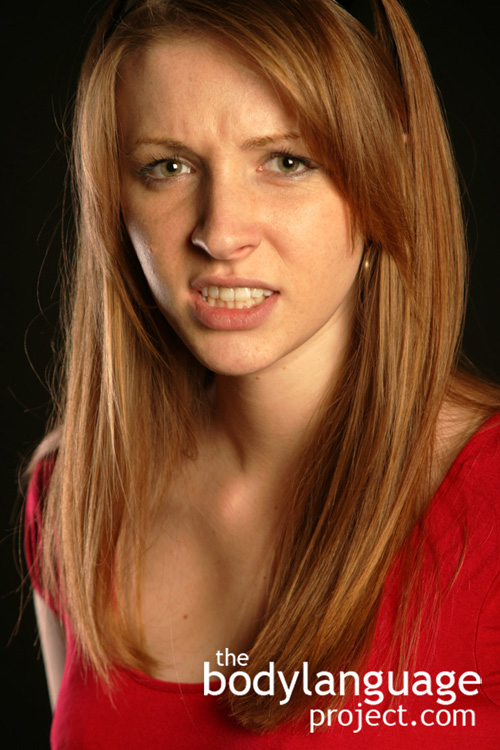
 Anger: Lowering the brow, flaring of the eyes and tightening of the mouth.
Anger: Lowering the brow, flaring of the eyes and tightening of the mouth.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
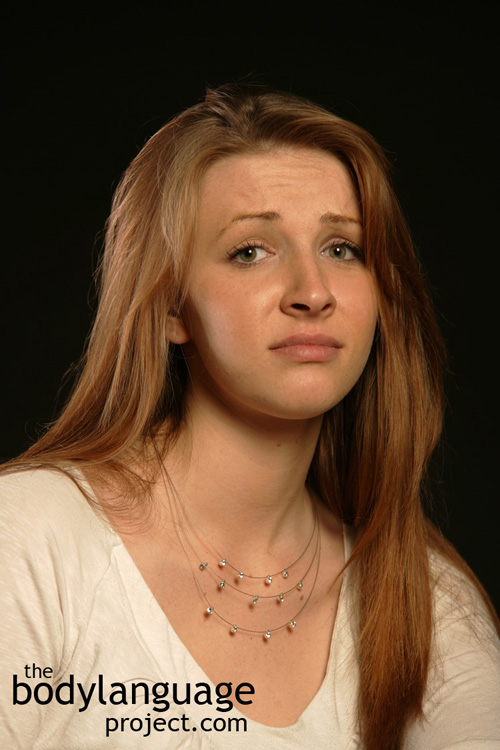
 Fear: Raising the upper eyelids and showing the whites of the eyes, raising the inner brow and folding the eyebrows inward (activation of the grief muscle), lowering the brow and or tightening of the eyelid. A grimace usually comes across the face.
Fear: Raising the upper eyelids and showing the whites of the eyes, raising the inner brow and folding the eyebrows inward (activation of the grief muscle), lowering the brow and or tightening of the eyelid. A grimace usually comes across the face.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
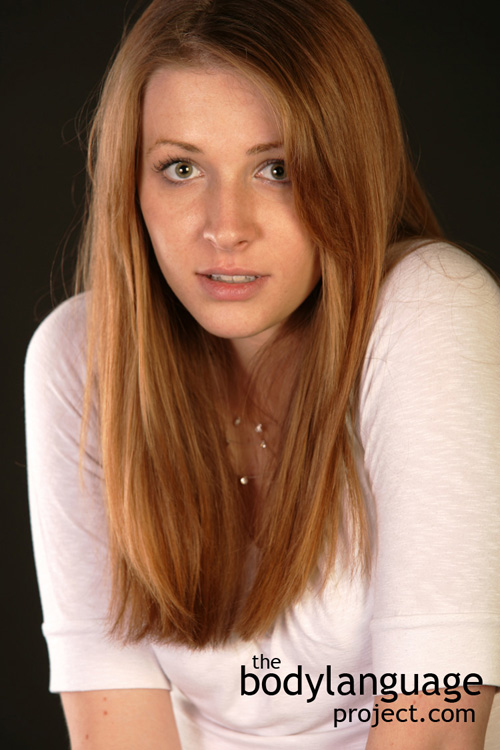
 Surprise: Straight upward lift of the brows.
Surprise: Straight upward lift of the brows.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
 Disgust: Baring of the teeth, lower of the eyebrows, tightening the eyelid, and wrinkling the nose.
Disgust: Baring of the teeth, lower of the eyebrows, tightening the eyelid, and wrinkling the nose.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
 Scorn: A combination of anger and disgust that happens by wrinkling of the nose, raising and tightening of the upper lip. To visualize this expression think of a bad smell.
Scorn: A combination of anger and disgust that happens by wrinkling of the nose, raising and tightening of the upper lip. To visualize this expression think of a bad smell.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
 Reverse smile: While smiling the corners of the mouth curl downwards momentarily displaying a caught/suppressed frown.
Reverse smile: While smiling the corners of the mouth curl downwards momentarily displaying a caught/suppressed frown.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
 False smile: Where the eyes play no part (no wrinkles in the corners of the eyes as in the Duchenne smile and the mouth is stretched across the face).
False smile: Where the eyes play no part (no wrinkles in the corners of the eyes as in the Duchenne smile and the mouth is stretched across the face).
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Doubt or disbelief: While answering a question in the affirmative saying “yes” the head is seen shaking from side-to-side in a ‘no-gesture.’
_____________________________________________________________________________________________