Objects can be erected to deflect emotional attacks.
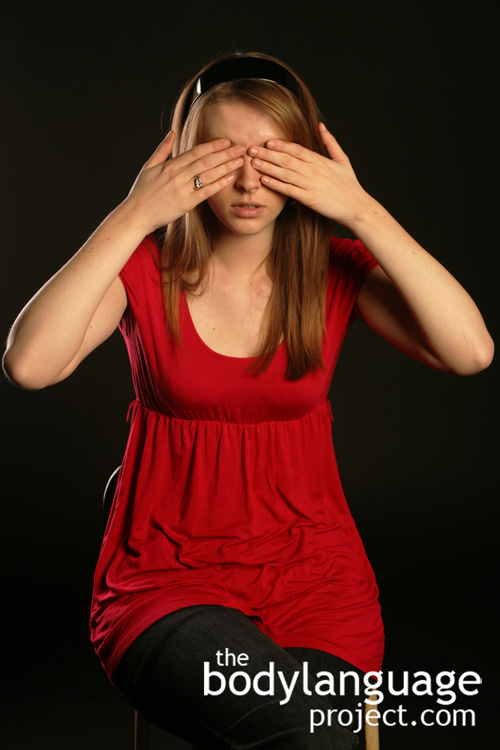
My wife frequently uses headphones in public places to avoid talking to strangers even if she isn’t playing music into them. If strangers come up to her, she points to her headphones as if to say that she can’t hear them. If she was really interested in a conversation, or minding other people’s business, she could remove them, but her point is that she isn’t. Headphones are therefore a strong message of introversion of which we wish not to be bothered. If a person strongly insists on interacting with her, she takes a long time to remove her headphones and accompanies it with irritated body language. She might even only partially listen to the person who has infringed on her privacy, although this is an advanced technique, before placing the headphones back on.
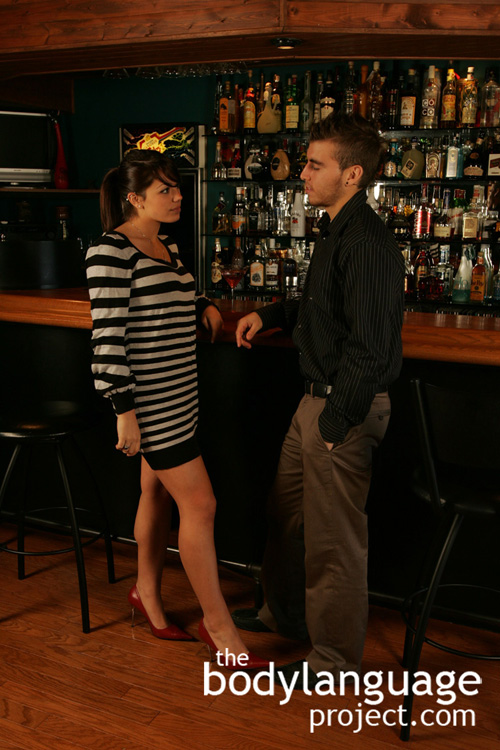
Now you might think that she’s being rude, but this is far from the case. She, like you, and everyone else, has the right to refuse to speak to whomever we please. We each owe no service to anyone else, especially interactions that were not mutually invited. Lack of eye contact in this case is a big factor in the right to refuse to interact. Dark eye glasses can close people out even more successfully, because it avoids accidental eye contact. Eye glasses make conversations shorter and less productive than one’s that occur when the eyes are exposed. Obviously, if we wish to welcome and continue a conversation or increase its effectiveness, we should promptly remove our sunglasses, even in really sunny conditions, so we might benefit from mutual gaze. When your counterpart wears glasses too, you might however, both agree to keep them on.
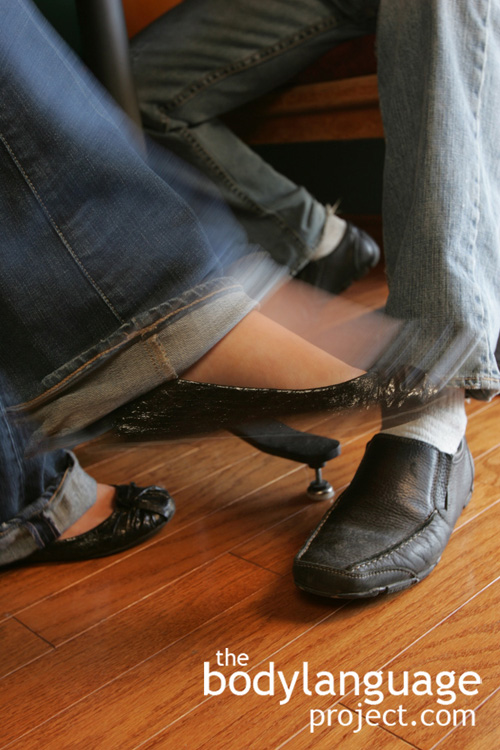
Barriers for negatively reasons are most common, but as in the peek-a-boo game that is played by men and women, objects can be used to tease and arouse in courtship. This is the case with “eye hiding”, which happens when a drinking glass, menu, or even people moving about a room temporarily put out of vision our object of affection. It can also happen by slightly turning away, or lowering the eyes coyly. Dropping the eyes out of sight or looking over the shoulder when done by women is particularly seductive. The loss of sight sends us into spells of worry, but when they suddenly reappear it sends our hearts races with relief. Small babies especially enjoy this game, sending them into giggle fits, and adults play along happily. When adults play the game with each other, it is only slightly more sophistication.
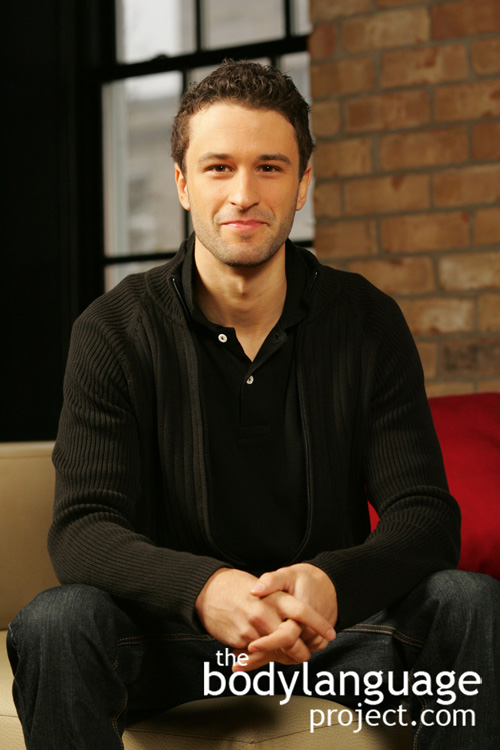
How one holds their arms while seated at a table can tell us the degree of acceptance or defensiveness they have toward us or our views. For example, having the arms apart indicates general agreement, having both arms parallel but uncrossed shows partial agreement, and having the arms folded on the table indicates disagreement. In this case, arms are being used as barriers. We have covered ways to break barriers and open those who show closed body language earlier. To reiterate though, we concluded that while it’s possible to open someone by offering them objects such as a drink or reading material to uncross their arms, it is usually best to openly address their concerns.
Improper use of barriers happen to all of us, because we aren’t totally aware or continuously conscious of their hidden meaning. Take a social gathering for example, where nearly everyone will have drinks and snacks on hand. How do we hold them while we stand, what about while we sit? While standing, more times than not, our arms are cocked at ninety degrees keeping our arm parallel to the floor to keep our drink upright preventing it from spilling. Unfortunately, this sends a bad message because it is a partially closed body position since it creates a barrier that isolates our bodies from others. While drinking alcohol can make people more social, having to hold the drink at the chest impedes our ability to use our hands properly and expressively. If you absolutely must drink or you think it is required to fit in with the crowed, then try holding your glass to your side so that you don’t block off the center-line of your body. If a table or bar top is nearby, use it to store your drink and so free your hands to gesture with palms up. While sitting at a table, feel free to put your drink to your flank so that you aren’t talking over it, and your arm, the entire evening. For a lot of people, drinks are crutches, something to hold on to, and as described earlier, are a form of security blanket. If you think you’re ready to “grow up”, try standing free form instead of toting your drink around at your chest. It’s not as easy as it sounds!
Objects as small as pens, but as large as books or newspapers, can be used to indicate division between people and create space between them. Just like the beverage example however, using the pen to write on a piece of paper by crossing the center-line of the body effectively closes it off. If no object is present at all, the barrier can still be formed by leaning on the table with both forearms and putting weight on them. This anchors and locks the barrier into the table. Although it is a closed message, it can be diminished to a degree by leaning forward toward your company. Holding the pen out and away from the body shows the opposite message. It is an indication that someone wishes to “extend” or offer an idea to them, and they wish their idea would cross the center-line of the table and enter into the other person’s ideology. The same sort of casual invasion of space, showing a desire to become connected, happens anytime the center-line cut evenly between two people, is breached. This can happen with reading material or business documents, hands in gesture, hands to touch, the sharing of food and of course love letters.
Conversations in busy places can be shut off completely just by raising a book and beginning to read. Sometimes this isn’t enough, so emphasis needs to be placed on it. We do this by peering rudely over them with an off-putting face and then slowly raising the reading material again. Obviously, this message is only rarely missed or ignored.
If you are the subject of unwanted blocking then begin by reviewing the pattern of communications that has lead to this result. Have you come on too strong? Were your ideas overly political or religious? Have you been too expressive or aggressive? Whatever the case, your best bet is to back-off and use relaxed body language to diffuse whatever anger you might have created. Ease the tension by taking a break and allowing your partner to have some emotional downtime. Try to devise a way to regain common ground, even if it means changing the subject or leaving it entirely to start fresh another day. Whatever you do, don’t bother trying to push your ideas forth too strongly, as they will simply be met with increased resistance. Finally, not everyone who uses barriers do so because they dislike other’s based on personal grounds, rather some just require more space and privacy, even in public.