The ankle or scissor cross is where the ankles cross each other and is a posture that can happen while seated or standing. While seated this posture is a hidden form of leg crossing because it occurs discretely at the bottom of the legs and can be out of sight due to a desk or table. While standing, it is the only way legs can cross so has a similar meant to a regular full blown seated leg cross. At times the leg might be raised up the backside of the calve producing the appearance of a flamingo but this posture is mainly reserved for women. While seated, the legs can also be locked behind the legs of a chair with essentially the same message being delivered except in this case it is a restraining-freeze-behaviour. When the legs are wrapped around the chair they can’t move, hence they are locked, and are also there precisely so they don’t move, and are hence frozen. Women are also seen using the sitting position more often them men especially if they are wearing skirts, however, it is not a confident posture so should be avoided. When it does happen in men though, it should be noted since it is an unnatural position in general for them.
The ankle cross indicates that the person is holding a negative emotion, uncertainty, fear, feels discomfort or threatened, stress, anxiousness, insecurity or timidity. The ankle or scissor cross also shows reservation and self-restraint,

Lots of cues in concert. Arms in a partial-cross coupled with crossed ankles – and he’s not doing much better as he ‘holds himself back!’
due to withholding of a thought or emotion. When being pitched, it shows resistance to the sale and when being questioned might indicate that lying is taking place. Couple interlocked legs, which is a freeze response meant to reduce foot movement, with pacifying behaviours such as rubbing the thighs palm down, as if to dry them, and you’ve got a cluster signaling that a secret is being covered. If the feet are pulled under the chair, the message is even more exaggerated. The feet are saying exactly what the person is thinking, that he or she is closed and withdrawn from the conversation. We should be watchful of this posture when presenting a controversial opinion to see what degree of disagreement is present and especially if the posture is held for a significant length of time, particularly by men. When the ankles cross it is due to a subconscious freeze response due to a threat and the legs are entwined so as to restrict and restraint movement.
As we saw previously, closing a sale or changing opinions necessitates open minds and since our bodies and minds are linked should try to open those with the scissor posture when possible. You could try to have them change positions, as above, by having them stand or relocate to a more comfortable seating location, or you could take the time to identify and address whatever issue is of concern. This is important especially if the posture preludes a more intense selling session to follow, since negative postures early on are a good predictor of the future.

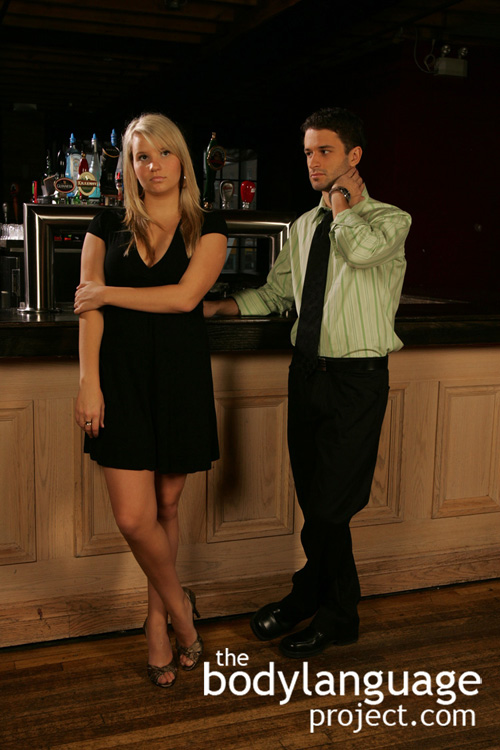
Mixed message – head cocked to the side shows interest coupled with arm and ankle crossing – she’s uncertain.
In a free-flowing interview or discussion noting the timing of ankle cross’ can prove valuable. With some research or prodding it might be possible to reveal the true reason for the action. Simply asking the reason for the reservation can help eliminate this posture as well because it will make the person feel listened. This is risky, though, because the primary reason for the gesture is to conceal an emotion. Conversely, giving someone the opportunity to express their thoughts makes people feel heard and sometimes that is all that is needed to open someone up. The posture after all, is a posture of hidden disagreement, so it would be hard to hold the posture as one is given the chance to open up. If the posture returns after some time, it might indicate that the person hasn’t fully disclosed their true opinion on the matter or that a new issue of contention has been uncovered. Therefore, once again, time should be taken to address any concerns that might have arisen before moving forward.