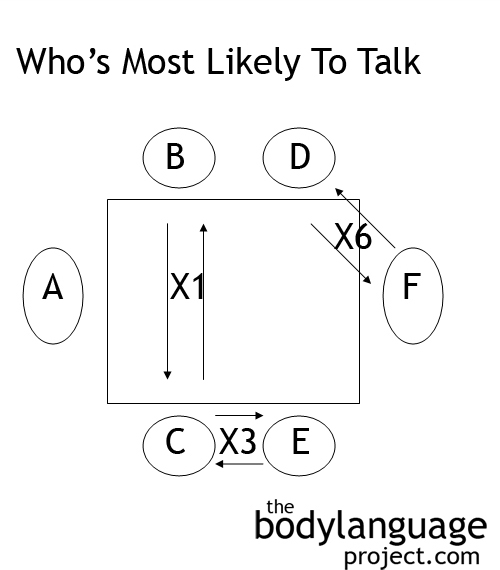
In a business setting people sitting kitty-corner (D and F) tend to talk 6 times as often as those sitting opposite (B and C). Those sitting next to each other (C and E) talk about half as often as kitty-corner but still 3 times as often as sitting on opposite sides of the table. The head position or leader position, tends to be spoken to the least.
One of the
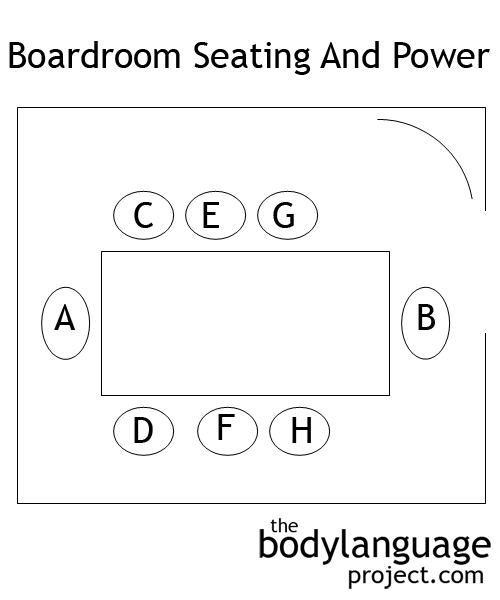
Boardrooms present an interesting power effect. In this case “A” is the head of the table because he benefits by seeing who might be entering through the door. “B” is also head of the table, but might be taken by surprise as the door is at his back. Power trickles down from the head of the table to “C” and “D” (flaking the head), “E” and “F” (flanking the flanks), and finally “G” and “H” who share the lowest rank..
earliest research studies was done by American psychologist Robert Sommer of the University of California in the 1950’s. He examined the effects of extensive renovations done to an old age home. The ward received new colourful paint, new lighting was installed, new chairs brought in and several small rooms were converted into one large day room. The furniture was also re-arranged to make conversations more likely amongst the patients by creating more face-to-face encounters. This rearrangement was based on what he observed daily in the hallways just outside the ward. Here, every morning the chairs were placed into straight rows, shoulder to shoulder, against the wall to make mopping easier. But if you entered sometime later in the day, you’d find them re-arranged into groups. It was the patient’s family members who moved the chairs to speak with the patients, rather than what the patient actually preferred themselves. From this observation and the fact that any changes in the ward were met with resistance it was obvious that the patients would resist the ward remodel. In fact, it was common knowledge around the home that every piece of furniture and chair “had its place.” A lot of which had been there, regardless of any logical or functional reason. The conclusions drawn from the study were less than positive likely because the study involved mentally handicapped patients. In fact, it was concluded that modification of furniture arrangements was not enough in and of itself to adequately increasing social interactions. However, drawing on his initial observations from the hallway, where regular visitors rearranged furniture, Dr. Sommer felt he was onto something important.
His future studies examined visitors interacting in a hospital cafeteria, students in classrooms, children in public, and a myriad of other social situations. He found that when conversing over a rectangular table, patterns began to emerge as a function of the shape and proximity speakers had to one another. In all arrangements it is the nature of the meeting which dictated the spatial “ecology”, he concluded. He learned that eye contact and distance are the two fundamental concepts governing how we sit, which in turn affects our ability to exchange information, speak effectively, or even draw lines of division. The next few paragraphs covers the ecology of round, and rectangular seating arrangements with respect to reasons for meeting, be it a casual meeting with friends, cooperative sharing of information, independent working or leadership purposes.
