Touch reduction is usually accompanied with stressful questions or when information is presented that creates anxiety. Closeness can also be useful when assessing someone because it will invoke distancing desires. When talking with a spouse or child, sit as close as that which you are accustomed to before taking up serious matters. If someone is hiding something, they will usually push away or even stand up looking for ways to exit or change the subject. Holding the hand of a child can be particularly useful when discussing matters of dishonesty. If they wish to exit the discussion, they will try to tug their hand away.
Tag Archive for Family Members
Early Research Into Seating Arrangements
by Chris Site Author • March 6, 2013 • 0 Comments
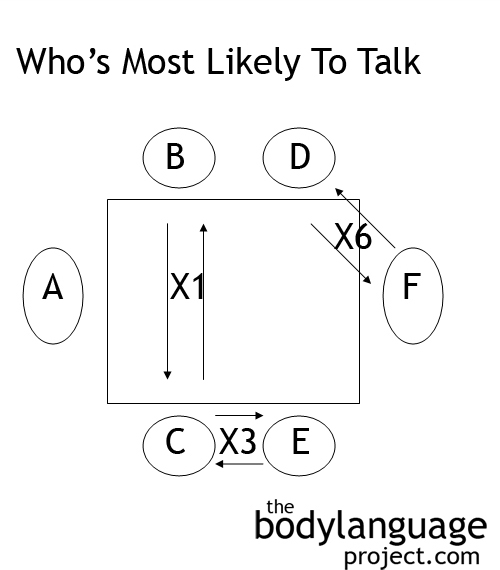
In a business setting people sitting kitty-corner (D and F) tend to talk 6 times as often as those sitting opposite (B and C). Those sitting next to each other (C and E) talk about half as often as kitty-corner but still 3 times as often as sitting on opposite sides of the table. The head position or leader position, tends to be spoken to the least.
One of the
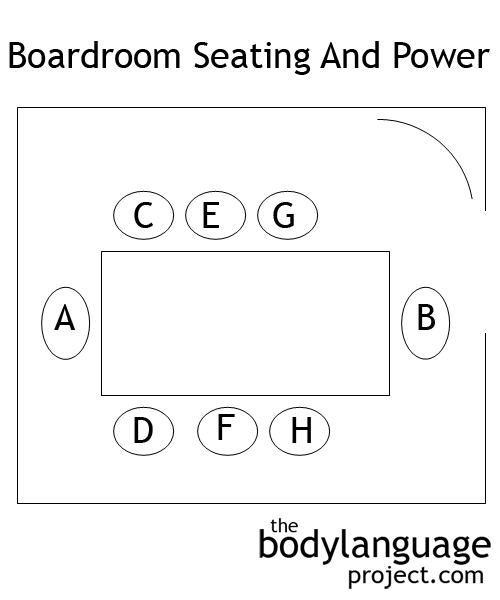
Boardrooms present an interesting power effect. In this case “A” is the head of the table because he benefits by seeing who might be entering through the door. “B” is also head of the table, but might be taken by surprise as the door is at his back. Power trickles down from the head of the table to “C” and “D” (flaking the head), “E” and “F” (flanking the flanks), and finally “G” and “H” who share the lowest rank..
earliest research studies was done by American psychologist Robert Sommer of the University of California in the 1950’s. He examined the effects of extensive renovations done to an old age home. The ward received new colourful paint, new lighting was installed, new chairs brought in and several small rooms were converted into one large day room. The furniture was also re-arranged to make conversations more likely amongst the patients by creating more face-to-face encounters. This rearrangement was based on what he observed daily in the hallways just outside the ward. Here, every morning the chairs were placed into straight rows, shoulder to shoulder, against the wall to make mopping easier. But if you entered sometime later in the day, you’d find them re-arranged into groups. It was the patient’s family members who moved the chairs to speak with the patients, rather than what the patient actually preferred themselves. From this observation and the fact that any changes in the ward were met with resistance it was obvious that the patients would resist the ward remodel. In fact, it was common knowledge around the home that every piece of furniture and chair “had its place.” A lot of which had been there, regardless of any logical or functional reason. The conclusions drawn from the study were less than positive likely because the study involved mentally handicapped patients. In fact, it was concluded that modification of furniture arrangements was not enough in and of itself to adequately increasing social interactions. However, drawing on his initial observations from the hallway, where regular visitors rearranged furniture, Dr. Sommer felt he was onto something important.
His future studies examined visitors interacting in a hospital cafeteria, students in classrooms, children in public, and a myriad of other social situations. He found that when conversing over a rectangular table, patterns began to emerge as a function of the shape and proximity speakers had to one another. In all arrangements it is the nature of the meeting which dictated the spatial “ecology”, he concluded. He learned that eye contact and distance are the two fundamental concepts governing how we sit, which in turn affects our ability to exchange information, speak effectively, or even draw lines of division. The next few paragraphs covers the ecology of round, and rectangular seating arrangements with respect to reasons for meeting, be it a casual meeting with friends, cooperative sharing of information, independent working or leadership purposes.
The Types Of Hugs
by Chris Site Author • March 6, 2013 • 6 Comments
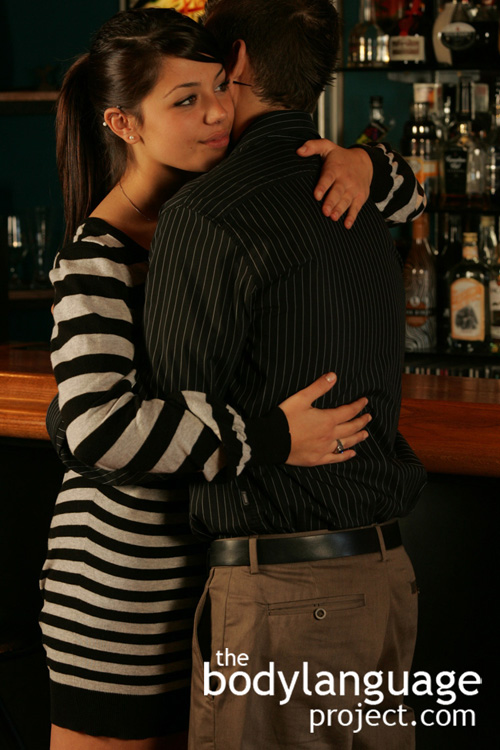

An intimate hug is obvious by checking the distance between the hips. The smaller the distance, the more intimacy is present. When we hug grandma, we might only touch shoulders by leaning in!
There are two types of hugs and each one indicates a different level of intimacy. The first is called the “full body hug” and is reserved for sexual partners. This type of hug is characterized by full chest to chest and hip to hip contact. Since the bodies are so tightly pressed together, the genitals might also touch incidentally. The second type of huge is the “light social hug”, the main hug for acquaintances and friends, and happens when the shoulders come together as the torso hunches forward, but the hips remain apart.
Hugs have a secondary hidden meaning as well. The longer the hug, the more intimate and affectionate is the relationship. A pat at the end of the hug indicates that one party would like to “submit” from the hug and terminate it. This gesture is similar to the actions wrestlers to do “tap out.” Taps also show feigned or meaningless hugs, or even unwelcome hugs, especially if the tap happens early. Most people think tapping while hugging shows comfort, but sexually romantic partners and close family members do not pat, they embrace deeply and squeeze tight.
The hips, during a hug, also have a very significant hidden meaning. That meaning is conveyed directly through the distance to which they remain separated and that distance tells us a lot about the type of relationship two people have. Hugs that happen between family and friends will have at least six inches between the pelvic regions of each person, whereas hugs from lovers have no, or very little space between the hips. The torsos of lovers also move tightly into each other’s intimate zones enveloping each other. The degree to which hips remain separate, or rear-ends are extended outward, whichever you prefer, and the amount of contact that takes place in the upper chest, tells us what degree of intimacy is present between huggers. Light hugs as we saw, can include only light shoulder contact, and in extreme light hugging, the bodies might not press together at all. The arms and hands might form a closed loop from shoulder to shoulder “around” them, but the chest and shoulders might only seem to move slightly closer, or seem to bob in quickly before moving out, not coming any closer than a foot. The hidden language of hugs can tell us a lot about the relationships around us, even potentially juicy ones like those brewing amongst staff members. A careful eye at the next social affair might uncover some cheeky relationships!
Touching Between And Amongst The Sexes
by Chris Site Author • March 5, 2013 • 0 Comments
Studies show that touching between men, especially in the workplace, is usually related to power plays and social jostling. An employer will place his hand on the shoulder or back of an employee to reaffirm his status while offering encouragement. Such displays are inappropriate in reverse and wouldn’t usually be tolerated. If touching is well received though, it indicates that strong rapport is being built between the ranks and a promotion might be forthcoming. Men can use touch, as a means to raise their status by initiating it against men of slightly higher status than them. If done tactfully, it can create a leveling effect and force them to reevaluate the rank they have attributed to you. If touching is done incorrectly, it will catch high status individuals off guard producing a negative effect that can be difficult or impossible to correct. Men, overall, rate touching less positively as a rule when compared to women, so touching initiated against men should be sparse.
Touching between men and women often outlines sexual interest and when women touch each other, it is often done out of friendship or to extend sympathy or formulate bonds. Family members also use touching such as hugs and kisses to display affection. Touching comforts are different from person to person and also of different cultures. The kiss hello for example is commonplace in Switzerland, Southern Europe, Latin America and the Mediterranean. It is uncommon in North America, Asia and some of Northern and Western Europe. Localized kiss hellos happens in Miami and Quebec for example and even in regional neighbourhoods such as with Italian or Hispanics. As far as hand holding goes, it is commonplace in the Middle East to symbolize friendship and respect when done between adult men. Even President George Bush was spotted holding Saudi’s crown Prince Abdullah’s hand which scored points with the locals, but became water cooler material for people in the U.S.
Personal Space Distances
by Chris Site Author • March 5, 2013 • 0 Comments
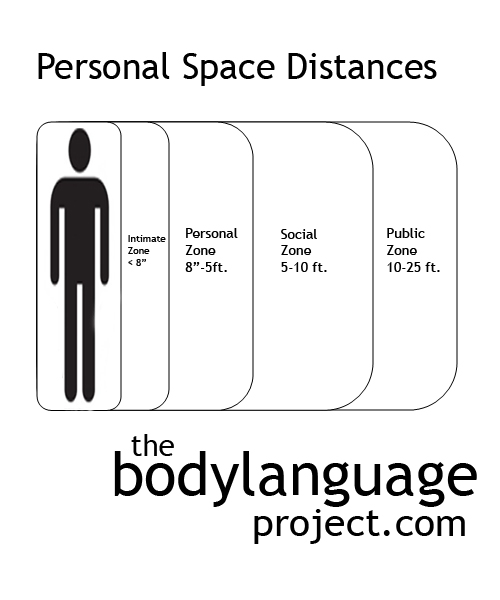
There are four distances by which people interact. They are the “intimate distance” where only about eight inches or less separates two people, the “personal distance” from eighteen inches to five feet, the “social distance” which is from five to ten feet and the “public distance” which is from ten feet to twenty-five feet. We tolerate intimate distances for embracing, touching, or whispering from sexual partners, family members and occasionally, even friends. Personal space is reserved for good friends and those we have a fairly high level of trust. The social distance is reserved for acquaintances that we perhaps don’t fully trust yet, but otherwise need to interact with, and the public distance is that which we use to address large audiences.

An arm is extended to indicate that personal space is being violated and protect a personal space bubble.
Our personal space, the area next to our bodies, which we protect against intrusion, has been referred to as a “bubble”, since it encircles us, but it more closely resembles a cylinder. The cylinder encompasses our entire bodies, from our feet to our head. It is this cylinder that we protect rigorously, and when it is violated we tense up or back away so as to reduce or prevent additional overlap from the cylinders of others. Our personal space isn’t totally fixed either. It is constantly expanding and contracting depending on our environment and company. For example, we permit children, pets, and inanimate objects into our personal space regularly because we do not perceive them as a threat, but other adults must earn our trust before entering. Our personal space tolerances are directly related to the strength of our relationship.
In basic terms, our personal space zone is the perimeter that we feel is suitable to act as a buffer should a dangerous situation arise. It provides us with enough time and space, we think, to react and mount a defensive posture to protect ourselves from an attack. In a busy public area, we might tolerate (although not prefer) moderate contact due to space limitations, but when space is abundant we see even mild intrusions as a predictors of an attack. Our personal space zone, therefore, is an early warning system that we use to help us predict the intensions of others.
These zones and distances are not immutable and universal, but are meant as a guide or rule of thumb. Everyone has different levels of comfort based upon their upbringing, personality type, gender, age and so forth. The summary listed below is a guideline that is meant for those living in areas such as Australia, Canada, United States, Great Britain and New Zealand or other westernized countries such as Iceland and Singapore or Guam. For other countries not listed, the zones may expand or contract based on the inverse of their density. For example, Japan and China which have a high density have smaller intimate zone distances. There is an inverse correlation to each zone, where the greater the population density, the tighter the zones.
The safest way to test a person’s need for personal space is to move close, lean in, give a hearty but not overly aggressive handshake, then take a step back to allow the person to either move in closer to shrink the space between you and them or take a step backward, to suite a larger than average personal space requirements. Too often people will move in too tight and overshadow someone else only to make them uncomfortable. If someone requires less space, they won’t feel offended to take up the space between you, and if you care anything about them, you won’t feel a need to step backwards either. Shrinking space is a way for people to tell you that they enjoy you, and your company, and one that you should not take offense to, but rather use as a measure of someone’s level of comfort.
1. Intimate zone – eight inches and less. This is our intimate space which we protect vigorously. We permit only those we trust emotionally to enter including parents, children, friends, lovers, relatives and pets. Lovers (and pets) are the only ones we permit to enter for any length of time, the rest we allow entry for only short instances such as for hugs.
2. Personal zone – eight inches to five feet. This is the distance from which we communicate to acquaintances; those we have achieved some level of trust. Examples include bosses and fellow employees, friends of friends, and so forth.
3. Social zone – five feet to ten feet. Normal for people on a first encounter such as people on the street asking for directions, a clerk at a store, strangers at a supermarket and other people we don’t know very well. Here we struggle between conflicting needs, one is to maintain enough space for comfort and the other is to be close enough to communicate effectively.
4. Public zone – ten feet to twenty-five feet. This is the zone at which it is comfortable to address a large group of people or audience during a presentation or speech. Even if we know all the members of the group well, we still maintain a greater distance from them so we can easily address all of them and keep everyone in our field of view. This could be an evolutionary adaptation since a large group could easily contain rogue defectors. By getting too close to an audience we risk surprise attack which is why we feel more comfortable with a wider buffer. Then again, it could simply be a function of judging the efficacy of our speech by measuring the audience’s reaction.