Body language is a fundamental part of courtship. As we have learned, verbal language is risky and not only because it may lead to embarrassment, but because it often requires a verbal response from others, which can turn out to be tragically embarrassing. Keeping spoken words out of courtship initiation process and therefore out of consciousness will save us plenty of grief from being openly rejected, or perhaps even worse, negative feelings with having to reject. Using and reading nonverbal cues therefore is important in courtship, so pay particular attention to the following signals so you can judge interest yourself, without saying a word. Courtship signals are extensive and complex, perhaps numbering in the thousands, so I will only cover the basics here. For those that want more detail, they may wish to read my e-book Body Language Project: Dating, Attraction and Sexual Body Language (2007). Much more emphasis is placed on instruction for men to help them read women better, although it can be helpful to women who wish to send more appropriate signals of attraction, rejection or to simply bring from the subconscious the signals they use all the time.
Tag Archive for Brains
Emotional Downtime
by Chris Site Author • March 6, 2013 • 0 Comments
It might not surprise you to know that everyone needs time alone every once in a while, or even once a day, but what might surprise you is that we actually need time to ourselves minute by minute. All day long we are bombarded with a multitude of people, from our coworkers, to our spouses, friends, to cashiers at stores and those who share our commute with us in the streets. Even with almost seemingly endless social interaction the research shows that every three seconds, on average, we ‘slip away’ to be with our own thoughts and to internalize what is happening around us. This ‘downtime’ allows our brains the time it needs to process, the information that is happening all around us.
We know someone is in downtime by their body language which includes having the head titled away or to the side, shifting the shoulders at an angle, or looking to the right or left for a fraction of a second. The eye patterns in downtime are what psychologists call ‘conjugate lateral eye movements.’ All these cues are tells that the mind has moved into processing mode and is no longer accepting new information. Other cues indicating emotional downtime include pauses in breathing, subtle chewing of the lips, or very brief eye freezes or glazing over.
Knowing about downtime can be used to our advantage so as to give people enough time to take in the new information presented rather than overwhelming them, confusing them and possibly putting them off for good. The simplest way to do this is to watch for downtime cues and then pause or slow speech accordingly. This will give the listener enough time to look away momentarily and process the information. Once we learn about someone, and their character, it will be easy to find their cues to downtime and therefore proceed at a reasonable pace for them specifically.
A second type of downtime is more extended, and happens in the absence of other people. The purpose of this downtime is to escape daily stress and pressure, and to help us recover. The need for downtime is obvious. We become stressed or over-stimulated, our thought process becomes hazy and we can’t think straight. Our faces will also become blank and expressionless, and our eyes will glaze over and be unmoving. Other times we feel under-stimulated and detached from what is going on around us, and feel that we need to get away to re-connect. During this period we begin to withdraw by avoiding eye contact, dropping our heads and shoulders, and switching off our ears. We may zone out in such a significant way that we have trouble even feeling someone if they happen to brush up against us. When downtime like this happens around other people we’re asked to ‘snap out of it’ only to reply with “Sorry, I was zoned out” or “I must have spaced out.” The most respectful thing to do when you notice someone in this state, is to leave them be, instead of interrupting them. Remember that they slipped into downtime for good reason, it’s not just to ignore you! In fact, as we saw, it has much less to do with negative reasons, than personal constructive ones. Downtime serves to relax the minds and set it back onto the right course before getting back to business.
Neck And Nose Body Language
by Chris Site Author • March 6, 2013 • 0 Comments
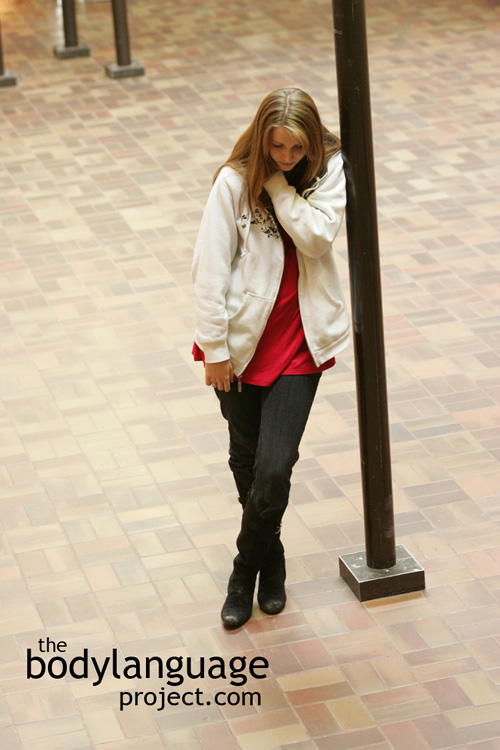

Covering the suprasternal notch is one of the nonverbal signals that is unmistakable and also reliable in predicting emotional distress, one that shouldn’t be ignored.
The neck is an area that becomes particularly sensitive under pressure and like the cheeks, it becomes red and engorged with blood when we become nervous. Women are particularly prone to bringing their hand up to the “suprasternal notch” which is the dimple just below the neck between the Adam’s apple and the breast bone when nervous, distressed, threatened, insecure, fearful or uncomfortable. Covering the suprasternal notch is one of the nonverbal signals that is unmistakable and also reliable in predicting emotional distress, one that shouldn’t be ignored.
While touching the neck and nose can be the result of fear or nervousness they can also be meant as pacifying behaviours. Pacifying behaviours happen automatically, our brains send a message to our bodies that we need to be pacified and out go our hands to serve the purpose. As always, it is important to decide what kind of emotion has demanded the body language, be it nervousness as a result of sweating (discussed below), or because there is an underlying threat causing fear that requires soothing.
Motioning toward our neck, scratching it, or pulling at a collar indicates we are “getting hot under the collar.” Humans sweat in response to external temperature increases but also due to emotional stress. In the case of emotional sweating, it is mostly restricted to the palms, soles of the feet and forehead. However, when we become emotionally aroused our metabolic rate revs-up and we burn more calories. This creates not just local sweating, but sweating throughout the body. Those under pressure can be seen sweating voraciously under the armpits and down their backs even leaving visible stains. Scratching the palms, in particular, has been shows to be a reliable indicator of stress but so too is scratching the neck. Scratching is in response to the tingling sensation we feel on our necks as the sweat increases and uncomfortable chaffing begins between tight collars and the skin. While some experts purport that sweating can indicate lying, it’s actually a signal of frustration and heightened emotion in response to pressure, and that this pressure can stem from anything, including simply being “put on the spot.”
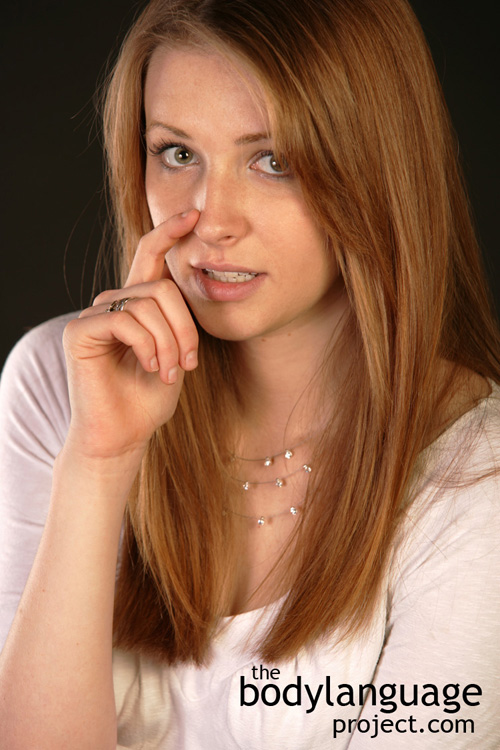
Our noses can also signal stress, but more often signal disgust. The nose is full of blood vessels so when we are stressed they fill up with blood just like the ears and neck. A person under stress will frequently go to their nose and touch it, scratch it or rub it. Touching the nose has been linked to lying, but like most lie detection cues, they aren’t absolute or reliable. We can tell when something is out of the ordinary when someone touches their nose for no reason. They might wipe it with the back of their hand or come up and touch it lightly with their index finger. The astute will find it obvious when someone is touching their nose for the purpose of alleviating an itch instead of alleviating a lie (or negative thought). Scratching is directed, specific, deep and vigorous, showing that some amount of waiting was done before the gesture was performed. Thus more relief is present when the itch is real. Itching due to negative emotions is general, shallow or glancing. This type of itch is done by bringing the index finger up, by example and lightly touching the side of the nose where the nail is not used at all. That is no real scratching is taking place.
Have you ever noticed how infrequently politicians touch their faces while in public and when they absolutely have to, they make it look deliberate and minimal? They raise just one finger and scratch a specific area, than they bring their hand back to their sides or use their hands to liven their speech. When trying to appear honest, we should follow their example. Keep face touching to a minimum, use it specifically, use the nail of the finger to show purposeful itching, and when finished resume normal open and honest gesturing.
When ready people for honesty, be careful not only to watch for cues, but also be watchful of cues that should be present, but aren’t. For example, if someone is describing emotional stress, they should exhibit classic nonverbal behaviours. A woman claiming to have swerved to miss an animal sending her automobile into the ditch should be agitate and on edge, perhaps covering her suprasternal notch as she recounts the details. Failing to exhibit the appropriate cues tells us that she might be trying to pull a fast one on us, perhaps trying to claim insurance so as to benefit from a payout. Looking for cues that should be there, but aren’t, are sometimes cues in and of themselves.
Hands And Palms Language
by Chris Site Author • March 5, 2013 • 0 Comments
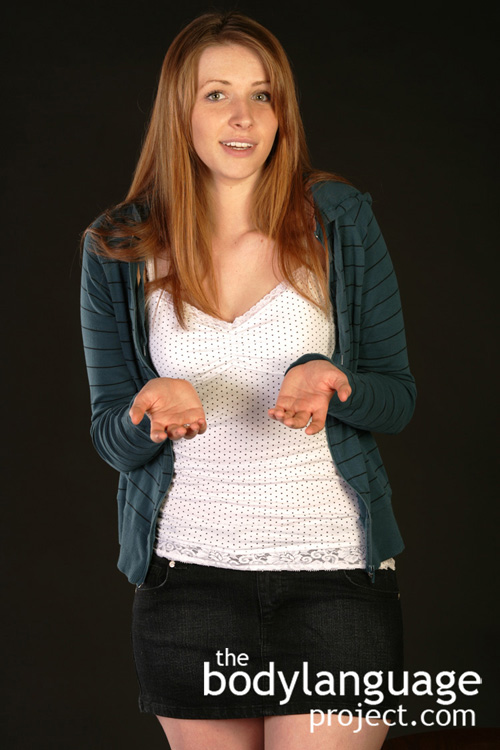

The “offerer” in the rogatory posture wants to give you his thoughts and just doesn’t understand your point of view.
The human brain has been shown to place a disproportionate amount of attention on the wrists, palms, fingers and hands compared to the rest of the body. Throughout evolution as we developed the ability to walk upright, our brains became fixated on what our hands were doing because they became more expressive in language through gesticulation, became more skilled such as creating fires, catching prey, collecting berries and building structures and tools to do so. However, our where our hands differ significantly from our feet is their ability to become extremely dangerous. Hands coupled with weapons can inflict deadly blows.
Being open means being honest and not hiding anything. In evolutionary terms, the palm display is an important gesture signifying honesty because it is a way to make evident to others that no threat or weapon is present. Palm and wrist displays have even been noted to be sexual in nature and more frequently flashed by women during courtship likely because it is such a vulnerable part of the body. The wave, as a long distance greeting, probably has roots in showing that we aren’t carrying a spear, sword, or bow and arrow. Having the hands deep in a pocket or behind the back can be a sign of aggression or passive threat, and our evolutionary history tells us that someone who is hiding something is probably not hiding a bouquet of flowers. But if they are, why take the risk! Showing open palms, facing up, or the “palm flash” is essentially what would have happened thousands of years ago when two foreign tribes met. Even today we might guess that a stranger approaching us on the street was up to no good if they hid their hands at their backs or tucked inside a jacket. We’d think they were harboring a gun and planned to rob us.
Having the arms out and extended, palms up, or vertical shows that we are safe and therein lies our most popular greeting, the handshake. The degree to which this openness occurs represents the degree of openness. Having the arms completely to the side or up and open with fingers apart is as open as one can get and it signal as much. We rarely see this form of openness, rather, openness is of degree, so we therefore must look for more subtle and acceptable cues.
Open gestures are accompanied by phrases such as “Trust me.”, “I wouldn’t lie to you.” and “What, you don’t believe me?” We also gesture with palms facing upward when we are offering something. However, the offering, in this context, isn’t a tangible item, rather, it’s an idea. It could be a cell phone plan coming from a salesman in the mall, or a reorganizing of the company, a downsizing, or new way to deal with customers or any number of things requiring deal making or selling.
When the arms are completely outstretched with palms up we call it the “rogatory” posture, or prayer-like. It is as if we are offering dialogue to another and sincerely want to be believed, trusted and accepted. This posture is not dominant or even confident however, because it lacks conviction. So while palm flashes show honesty and trustworthiness because they show no threat, they lack sustenance and power in terms of conviction. Palm down displays though, by placing hands face down on a table or standing head on and leaning with the fingertips spread to anchor the body shows emphatically that a position is held confidently. While conversing on a topic, we should therefore expect both palms up and palms down as opinions are either offered with reservation or presented with conviction. Depending on your position on the matter you may wish to employ either submission or dominance to your advantage. For example, on issues you wish to concede or are unsure of, of which making the other party aware of this fact is acceptable, use palm up, but when you wish not to concede or wish not to be uncovered as unsure, keep palms face down. The rule of thumb is that palms down “tell”, while palms up, “offer.” When someone wishes to display honesty, such as declaring “You have to believe me, I didn’t do it” they should use palm down displays otherwise they may not be telling the truth and expect not to be believed.
So why do we find it comfortable to put our hands in our pockets? Our clothing, especially that of men’s, is specifically designed with this in mind. The fashion of women rarely permits the luxury of the same deep pockets, but this isn’t to say they wouldn’t take advantage of them if they could. Curiousity says that we must reason why this is so. What is it about this hand placement that makes us more at ease? Are men more reserved to the point of requiring their garments to accommodate their needs or is it just superfluous? There’s no doubt that form meets function in this case, and putting our hands in our pockets makes us feel more comfortable and gives us a way to occupy our hands, but what does the body language convey to others?
When children lie they can be found to place their hands behind their back concealing them. This is a dishonest gesture. As we grow into adulthood, this gesture becomes more condensed and our hands find a new place in pockets. Seeming outright dishonest for having your hands buried in pockets is a bit extreme, but context specific could be a ‘tell.’ Regardless though, hidden hands convey a lack of confidence especially when the hands would be best served to gesture appropriately in conversation. The hands are a very effective way to colour our dialogue and make us appear more honest and intelligent. When delivering important information showing the flesh of the palms, the “palm flash” can be critical to portray honesty. At a subconscious level, as the palms are made more visible, the more honest others will find the speaker. Give it a try!
Origins Of Laughs And Why Laughing Is Addictive
by Chris Site Author • March 5, 2013 • 0 Comments
Some researchers conclude that laughs are a modification of the fear response which they theorize grew out of an historical warning that danger was near. By this theory, the laugh occurs because our brains are scared or frightened into laughing. This helps to explain why we often come to tears when laughing for prolonged periods, why we sometimes laugh when scared, or when we deal with horrific events such as a death by suddenly laughing, instead of a seemingly more appropriate response.
Strangely as it might sound, laughing is usual for people during periods of stress and uncertainty. We just laugh it off. Other theories say that laugh came about through a relaxed open play face which is similarly observed in other primates. Chimpanzees and Barbary macaques, for example, show a similar breathing sound “ahh ahh ahh.” Laughing in other primates comes from mock fighting, and social play and in humans, it first appears at one to two months of age and happens during tickling or sudden appearance of novel stimuli as in the peek-a-boo game. My son’s first laughs came about through fear. It was the only way we could get him to laugh. Even now, he laughs when startled such as in the peek-a-boo game.
Researcher Robert Provine describes the laugh as a series of short vowel-like notes or syllables, each being about seventy-five milliseconds in duration that repeat at regular intervals separated by about two hundred ten milliseconds. Laughs go something like “ha-ha-ha” or “ho-ho-ho” but never “ha-ho-ha-ho”. We can see other variations though like “cha-ha-ha” or “ha-ha-ho”. Laughs also tend to punctuate points or sentences and rarely find themselves mid sentence. His research outlines even more complexities in the laugh and if you are particularly interested in laugh structure I urge you to seek out his research, it is quite fascinating.
Laughing can become addictive too, since it releases natural pain killers called endorphins which give us a natural high. Thrill seekers such as sky divers, or race car drivers and even runners, and those who exercise regularly, also reap the rewards of the natural endorphin rushes. Endorphins have been shown to be stronger then morphine as a pain killer so activities like mentioned above can become habit forming. Being around people that make us laugh and smile gives us a positive outlook on the world. Similarly, being around people that are consistently frustrated, bring us down, as we empathize with their emotions. Our autonomic nervous system responds to our environments and the people in it which is why it is important to surround ourselves with people that make us feel good. Conversely, we can become the person others seek to initiate positive feelings, so taking the time to make someone laugh can have a huge payoff.
Eye Direction, Thought And NLP
by Chris Site Author • March 5, 2013 • 0 Comments
Eye movements are well known in neuro-linguistic programming abbreviated NLP, a system developed to help induce behavioural changes and improve communication between colleagues as well as to retrain thinking in business. It was developed in the 1970s by two researches in California, Richard Bandler and John Grinder who noted that the predominant research into human behaviour focused on problems rather than on solutions. NLP rather, focuses on the behaviour of successful people and is thought that by copying them, others too, can be successful. “Neuro” refers to the fives senses (hearing, touch, smell, sight, taste) “Linguistic” refers to the use of language to order thought and behaviour and “Programming” reflects the way ideas and thought are organized into actions. NLP is driven by defining positive outcomes, understanding how other’s perceive particular circumstances, and in identifying the roots by which thoughts affect images, sound or feelings.
It was discovered through experiment that eye movement is related to that part of the brain people where accessing. It began when researches noticed that the brain processed different information in different hemispheres. It was found that right handed people tended to shift their heads and eyes to the right during “left hemisphere” tasks such as logical and verbal processing and left handed people had entirely opposite patterns.
A typical left-handed person would have the opposite meanings for their eye-directions. Therefore, people tended to look to the opposite sides of the brains for the answers. Eye movements in this way, is one of the most well known but also the most controversial discoveries of NLP. It might also be one of the most valuable. The researches attached electrodes to subjects to track eye movement and brain wave characteristics. They were then asked questions related to sight, hearing or feeling tasks that involved memory or right brain processing and mental construction or left brain processing. Eye movement was shown to be related to how people process information. For example, upward eye movements reflected visual processing, lateral eye movements reflected auditory processing and downward movements reflected either kinesthetic (touch) or an inner thought or feeling.
So How Exactly Do The Minds Of Men And Women Differ?
by Chris Site Author • March 5, 2013 • 0 Comments
 Dr. Gurian believes there are about a hundred structural differences between the male and female brain. Men tend to compartmentalize their communication into smaller parts of the brain and therefore tend to get right down to the issues whereas women’s brains gather a lot more information from different areas of the brain and therefore tend to be more detailed in their conversations. Men also show more activity in mechanical centers of the brain and females show more activity in verbal and emotional centers. These changes happen very early in boys and girls. To a little girl, a doll becomes life-like with desires, feelings, needs or in other words a life, but to a little boy, that same doll is simply an object.
Dr. Gurian believes there are about a hundred structural differences between the male and female brain. Men tend to compartmentalize their communication into smaller parts of the brain and therefore tend to get right down to the issues whereas women’s brains gather a lot more information from different areas of the brain and therefore tend to be more detailed in their conversations. Men also show more activity in mechanical centers of the brain and females show more activity in verbal and emotional centers. These changes happen very early in boys and girls. To a little girl, a doll becomes life-like with desires, feelings, needs or in other words a life, but to a little boy, that same doll is simply an object.
The brain scans of women show that the corpus callosum which handles communication is larger than that of men’s. The corpus callosum is an anatomical part of the brain that is centered between the left and right hemisphere and helps women’s brains “talk” better across each hemisphere. The corpus callosum is a thick collection of nerve fibers that conduct information. In essence, it helps women multi-task by sending information to an fro, from one side to the other to be dissected, disseminated and refabricated as it is put through various brain centers. Men on the other hand tend to move information within the same side of the brain better and tend not to confuse issues with others. Women’s brains easily move from the right side (creative) to the left side (logical) and vice versa, very easily. This is why they often inject all sorts of emotions into their arguments and details into stories whereas men get stuck on the facts and logic and progress from A to B to C. Because of this ease of movement women can perform more operations at the same time, they can pick berries, take care of their young, and discuss camp ethics all at the same time. As it applies to our nonverbal discussion, it means that they can focus on more than just the words being spoken, they can also monitor body language as well.
So what does this all mean? Well, in practical terms, it means that women might have a better natural ability to read people. However, this book isn’t about what’s natural, it is about what can be learned and just about anyone can learn to read body language well, even if they are at an inherent disadvantage.
The Evolutionary Differences Between Men And Women
by Chris Site Author • March 5, 2013 • 0 Comments

We rarely catch women checking men out because they can always see the ‘whole picture’ unlike men and their predatory hunter eyes.
The hunter gatherer theory of human sex differences describes that men have evolved to be hunters whereas women have evolved to be gatherers. By this theory, the brains of men and the brains of women have been created under different selection pressures. The female mind was focused on language and communication especially between other females (gossip) and on searching out multiple food items, such as berries, vegetables and nuts. Men where more focused on tracking down prey, a single item, and used far less dialogue since talking too much might upset the animals they were pursuit. Once a successful plan was hatched amongst a group a men, spoken words were no longer necessary. Women, on the other hand, had to keep each other abreast of which fruits were in season and their location. The research supports this as women use landmarks and memorize routes to connect familiar places to navigate, even in cities, whereas men use more spatial factors such as direction of travel and the patterns of the roads themselves. Presumably it would be easier to describe to someone else how to go about finding berries in the wilderness through landmarks over a sense of the hills and terrain. For women, the food they gather doesn’t move, but men needed to be move about and orient an environment that was always changing based on the prey they were hunting and the season. Landmarks while hunting become useless when in new areas.
Men also tend to score higher on three-dimensional tasks such as moving an object in their minds to match similar items, a task called “mental rotation”. This spatial skill is attributed to throwing accuracy as one might use to fall moving prey. In tests, women perform better on language oriented tasks such as verbal memory and verbal recognition of sounds. Gossip amongst women around camp would have played a key role to protect unity, maintain peace and uncover dissenters. Women have also been shown to be more proficient at using both hemispheres of their brains since their left and right sides are better connected. Women can therefore use their minds more fully and draw from many centers of their brain.
The ability to use both hemispheres makes it much easier for women to work out complex relationships between people and their environment simultaneously. It fascinates me to listen to my wife click away at a game of solitary on her computer while she talks with her mom on the phone. Without pause the dialogue continues, whereas when I speak to my brother on the phone, and he’s watching television, the line practically goes dead! Body language requires a lot of focus and attention and women have much more mind to draw on to analyze it. Women seem therefore more naturally attuned to reading body language subconsciously, but that doesn’t mean it can’t easily be learned as is the case with my wife and I. By far, I am more aware of body language, due in large part to the amount of research I have done. My experience makes up for what I lack in brain power!
Women have a much wider visual field then men. That is, they can see further out on the periphery while still fixated on a central point. This is why women are so much better at finding things in the cupboard or in a drawer. Men’s eyes have pin point or tunnel vision and must look from one object to another eliminating them in sequence just to find what they need whereas women can see the whole picture all at once and identify the object needed. This partially explains why men find it so frustrating to have their things moved about the house when women tidy up. Men simply can not find them if they are relocated, but it’s not as if we don’t appreciate the effort! Conversely, women have difficulty pointing out and following moving objects such as animal in the woods or baseballs. With training however, both can become better at each task, the point is that men and women are inherently different, acknowledging our deficiencies just makes us each easier to live with! Having a better peripheral vision also explains why women don’t ever seem to stare at the men’s “junk” whereas men drop their gaze routinely to check women out. Women do check out other men, they just don’t get caught!












