There are four distances by which people interact. They are the “intimate distance” where only about eight inches or less separates two people, the “personal distance” from eighteen inches to five feet, the “social distance” which is from five to ten feet and the “public distance” which is from ten feet to twenty-five feet. We tolerate intimate distances for embracing, touching, or whispering from sexual partners, family members and occasionally, even friends. Personal space is reserved for good friends and those we have a fairly high level of trust. The social distance is reserved for acquaintances that we perhaps don’t fully trust yet, but otherwise need to interact with, and the public distance is that which we use to address large audiences.

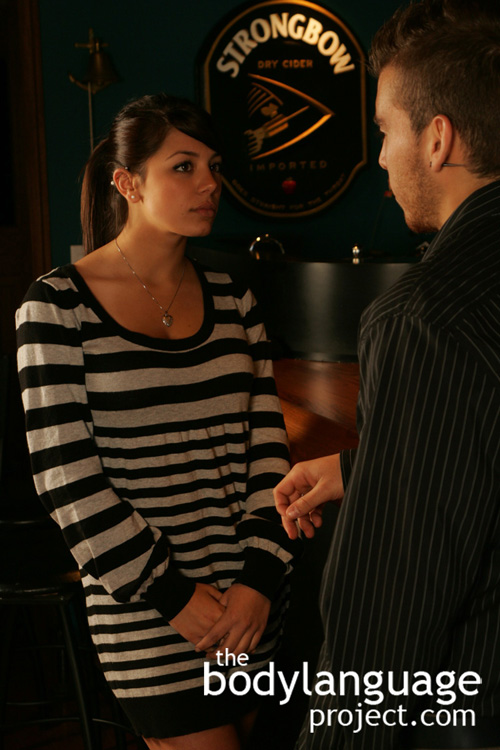
An arm is extended to indicate that personal space is being violated and protect a personal space bubble.
Our personal space, the area next to our bodies, which we protect against intrusion, has been referred to as a “bubble”, since it encircles us, but it more closely resembles a cylinder. The cylinder encompasses our entire bodies, from our feet to our head. It is this cylinder that we protect rigorously, and when it is violated we tense up or back away so as to reduce or prevent additional overlap from the cylinders of others. Our personal space isn’t totally fixed either. It is constantly expanding and contracting depending on our environment and company. For example, we permit children, pets, and inanimate objects into our personal space regularly because we do not perceive them as a threat, but other adults must earn our trust before entering. Our personal space tolerances are directly related to the strength of our relationship.

When space is invaded, we pull back.
In basic terms, our personal space zone is the perimeter that we feel is suitable to act as a buffer should a dangerous situation arise. It provides us with enough time and space, we think, to react and mount a defensive posture to protect ourselves from an attack. In a busy public area, we might tolerate (although not prefer) moderate contact due to space limitations, but when space is abundant we see even mild intrusions as a predictors of an attack. Our personal space zone, therefore, is an early warning system that we use to help us predict the intensions of others.
These zones and distances are not immutable and universal, but are meant as a guide or rule of thumb. Everyone has different levels of comfort based upon their upbringing, personality type, gender, age and so forth. The summary listed below is a guideline that is meant for those living in areas such as Australia, Canada, United States, Great Britain and New Zealand or other westernized countries such as Iceland and Singapore or Guam. For other countries not listed, the zones may expand or contract based on the inverse of their density. For example, Japan and China which have a high density have smaller intimate zone distances. There is an inverse correlation to each zone, where the greater the population density, the tighter the zones.
The safest way to test a person’s need for personal space is to move close, lean in, give a hearty but not overly aggressive handshake, then take a step back to allow the person to either move in closer to shrink the space between you and them or take a step backward, to suite a larger than average personal space requirements. Too often people will move in too tight and overshadow someone else only to make them uncomfortable. If someone requires less space, they won’t feel offended to take up the space between you, and if you care anything about them, you won’t feel a need to step backwards either. Shrinking space is a way for people to tell you that they enjoy you, and your company, and one that you should not take offense to, but rather use as a measure of someone’s level of comfort.
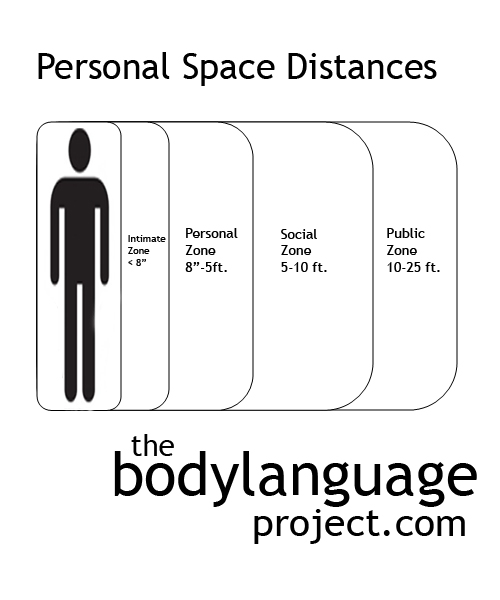
Personal Space Distances
1. Intimate zone – eight inches and less. This is our intimate space which we protect vigorously. We permit only those we trust emotionally to enter including parents, children, friends, lovers, relatives and pets. Lovers (and pets) are the only ones we permit to enter for any length of time, the rest we allow entry for only short instances such as for hugs.
2. Personal zone – eight inches to five feet. This is the distance from which we communicate to acquaintances; those we have achieved some level of trust. Examples include bosses and fellow employees, friends of friends, and so forth.
3. Social zone – five feet to ten feet. Normal for people on a first encounter such as people on the street asking for directions, a clerk at a store, strangers at a supermarket and other people we don’t know very well. Here we struggle between conflicting needs, one is to maintain enough space for comfort and the other is to be close enough to communicate effectively.
4. Public zone – ten feet to twenty-five feet. This is the zone at which it is comfortable to address a large group of people or audience during a presentation or speech. Even if we know all the members of the group well, we still maintain a greater distance from them so we can easily address all of them and keep everyone in our field of view. This could be an evolutionary adaptation since a large group could easily contain rogue defectors. By getting too close to an audience we risk surprise attack which is why we feel more comfortable with a wider buffer. Then again, it could simply be a function of judging the efficacy of our speech by measuring the audience’s reaction.















